Introduction: The Soviet Timekeeping Icon
The Raketa Big Zero is far more than a mere timepiece; it represents an iconic symbol of Soviet design and a tangible fragment of history. Its distinctive, minimalist aesthetic, characterised by oversized numerals and a prominent “0” at the 12 o’clock position, has captivated collectors worldwide. This design, initially conceived for practical reasons, transcended its original purpose to become a cultural landmark, particularly during the Perestroika era.
This report aims to delve deeper into the Raketa Big Zero, exploring its complex history, diverse models, and technical specifications. It intends to uncover lesser-known facts, verify existing information, and provide a comprehensive comparative analysis between vintage and modern iterations. Furthermore, this guide seeks to equip collectors with essential authentication advice, aiding them in navigating the intricate market of Soviet-era watches.

I. The Petrodvorets Watch Factory: From Imperial Origins to the Birth of Raketa
Foundation and Link to Peter the Great (1721)
The Petrodvorets Watch Factory, the birthplace of Raketa watches, boasts a remarkably long and distinguished history, with its origins tracing back to 1721. It was established by decree of Emperor Peter the Great, initially as a lapidary factory specialising in the processing of precious stones and jewellery. This imperial heritage underscores the factory’s deep roots in Russian craftsmanship and its historical significance, predating many renowned Swiss watch manufacturers. The factory is still housed in its original building in Peterhof (Saint Petersburg).
The factory’s founding by Peter the Great in 1721 and its continued operation in the historic Peterhof building indicate a strong emphasis on historical continuity and national pride. This is not merely a watch factory; it is an institution deeply intertwined with Russia’s history and achievements. This long and unbroken lineage, which even spanned the Soviet period, bestows a level of prestige and authenticity that many newer brands lack. This characteristic serves as a powerful positioning tool for the modern Raketa brand , also suggesting a deep accumulation of generational skills and knowledge, a distinguishing factor in an industry where many companies outsource production.
The Naming of “Raketa” in Honour of Yuri Gagarin (1961)
The brand name “Raketa” was established much later, in 1961, to commemorate a pivotal moment in human history: Yuri Gagarin’s first manned space flight aboard Vostok 1. This naming decision, meaning “Rocket” in Russian, directly linked the watches to Soviet innovation and industrial might, positioning them as symbols of national achievement.
The choice to name the brand “Raketa” in 1961, following Gagarin’s flight, proved to be a strategic branding move during the Cold War. This decision immediately associated the watches with Soviet technological triumphs and national pride. However, this association also generated a negative perception in the West, where “Raketa” was linked to intercontinental ballistic missiles. This dual perception highlights how deeply the brand was intertwined with the geopolitical context of the era, transforming a consumer good into a subtle propaganda tool. This historical context adds significant depth to the brand’s narrative for collectors.
Raketa’s Role in the Soviet Era: Production for Military, Explorers, and Civilians
During the Soviet era, Raketa watches were not mere consumer goods; they served critical functions for various state entities. They were produced for the Red Army, the Soviet Navy, and for North Pole expeditions, indicating a focus on robustness and reliability in extreme environments. Specialised models like the “Polar” (1969), with a 24-hour movement, were specifically designed for Arctic explorers to distinguish day from night. The factory also holds the world’s largest collection of watch design archives. The “Baikonur” model, designed in collaboration with cosmonaut Sergey Krikalev, featured special functions necessary for space travel. Raketa also collaborated with major aircraft manufacturers like Sukhoi and Tupolev to develop watches for pilots. At its peak in the 1970s, Raketa was among the world’s largest watch manufacturers, producing approximately five million mechanical watches annually.
The extensive production of watches for the military, navy, and explorers , coupled with the development of specialised models like the “Polar” and “Baikonur” , demonstrates that functionality and durability were absolute priorities in Soviet design, often outweighing luxury or aesthetic embellishments. This approach starkly contrasts with Western watchmaking, which tended to emphasise prestige and elaborate complications. This “function before flourish” philosophy, born out of necessity and state-controlled production, holds a strong appeal for many modern collectors of Soviet watches , offering a unique blend of history and robust engineering. This also implies a high standard of internal quality control, given the critical nature of these watches’ applications.
Post-Soviet Revival (2010) and Commitment to In-House Production
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Raketa faced significant challenges in adapting to a market economy. However, its fortunes began to change in 2010 with a revival led by British entrepreneur David Henderson-Stewart. Under new management, Raketa adopted modern production methods while preserving its heritage, notably by continuing to produce its mechanical movements entirely in-house, “from A to Z”. This commitment to vertical integration, including the production of hairsprings and escapements , is a rare feat in the global watch industry, distinguishing Raketa from most brands that rely on external suppliers like Nivarox. The factory even attracted former Rolex and Breguet watchmakers to modernise its production.
The post-Soviet revival led by David Henderson-Stewart and the renewed focus on in-house movement production represent a strategic move to reposition Raketa in the global luxury market. In an industry where “manufacture” status is highly valued, Raketa’s ability to produce its own hairsprings and escapements provides a strong narrative of authenticity and a competitive advantage over brands that merely assemble external components. This commitment to traditional watchmaking, combined with a modern marketing approach, allows Raketa to appeal to both vintage watch enthusiasts and new collectors seeking genuine horological value.
II. The “Big Zero”: Design Genesis and the Gorbachev Legend
The Original 1970s Design and Its Minimalist Aesthetic
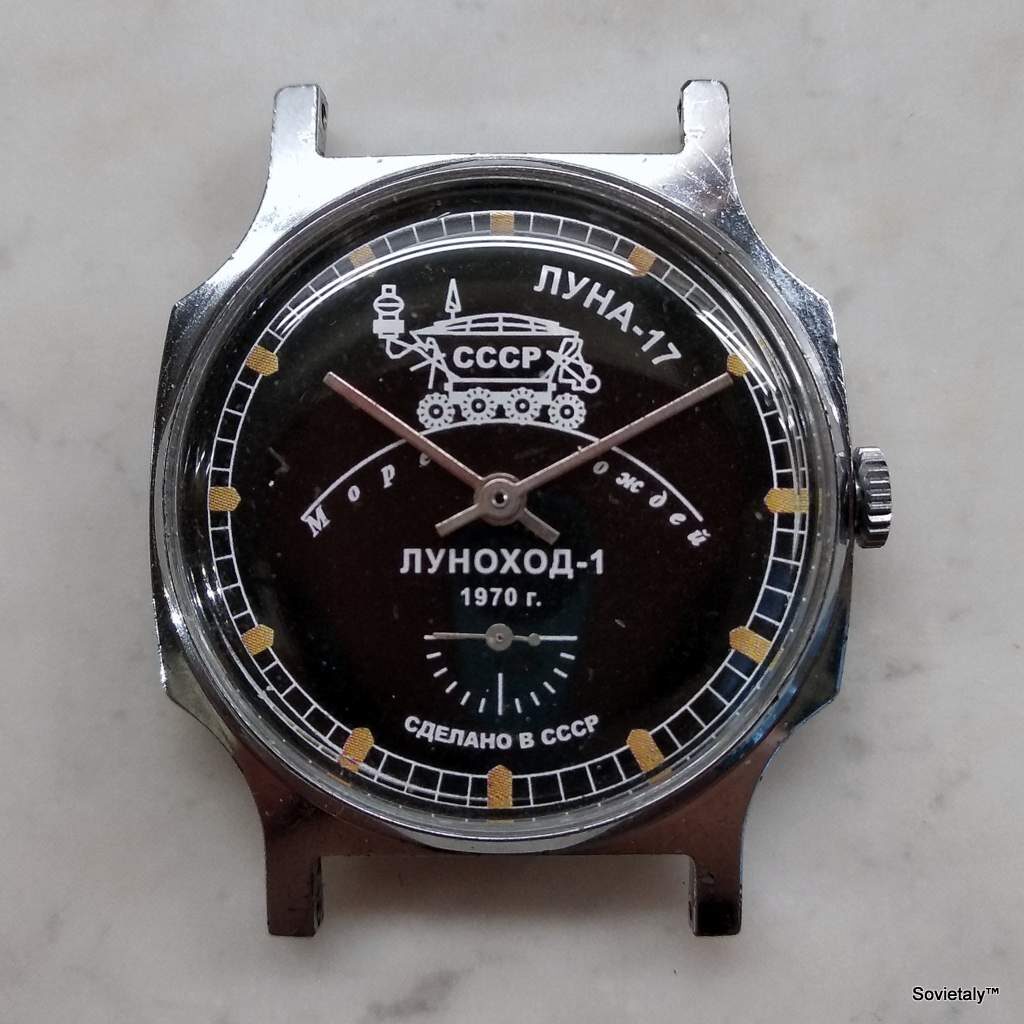
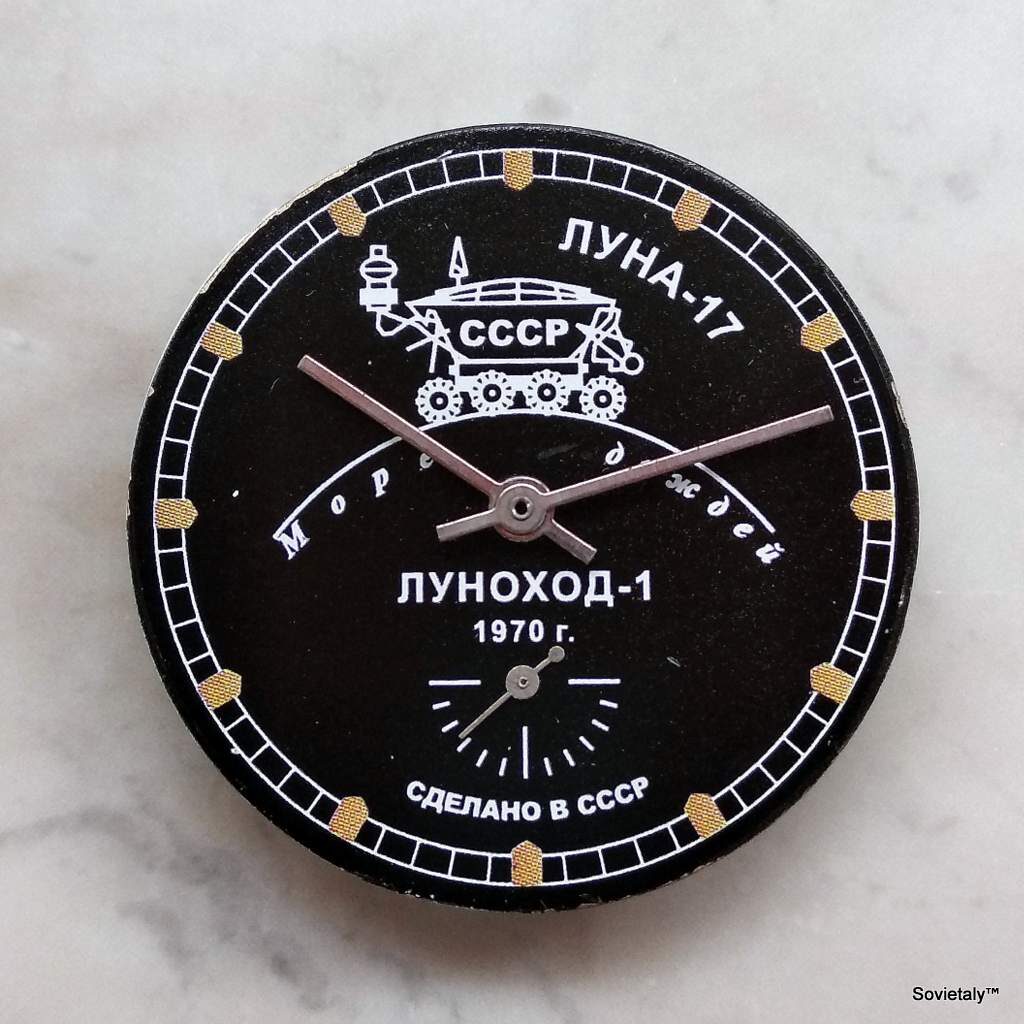
The original design of the Raketa “Big Zero” dates back to the 1970s. Its aesthetic is distinctly minimalist, characterised by a clean, uncluttered dial with oversized numerals for 3, 6, 9, and a prominent “0” at the 12 o’clock position. The other hour markers are typically represented by long, narrow triangles. This bold, almost “brutal” yet functional design, with its high-contrast black and white colour scheme, ensured excellent legibility.
The “Big Zero” design, originating in the 1970s , with its oversized numerals and the “0” at 12 o’clock, was initially conceived for practical purposes, such as making it easier for visually impaired individuals to read the time or ensuring clear time indication in challenging conditions. This emphasis on legibility and functionality aligns with the broader Soviet design philosophy, where utility often took precedence over ornamental aesthetics. The enduring appeal of the design lies precisely in this radical simplicity, which, ironically, has made it a timeless classic.
The Philosophy Behind the “0” Instead of “12”: Functionality and Symbolism
The most striking feature, the “0” instead of “12”, is not merely a design quirk. According to seasoned experts from the Raketa factory, it is rooted in a logical principle: “it is simply more logical to start counting time from zero. After all, time, like many aspects of our lives, invariably begins from zero”. This “rebellious concept” challenges traditional timekeeping norms, expressing a philosophical statement about new beginnings.
While it might appear to be a simple design choice, the “0” at 12 o’clock possesses a deeper, almost subversive utility. It is a pragmatic approach to time-telling that also embodies a philosophical statement about starting anew. This “zero” concept, coupled with the watch’s later association with Perestroika, gives the “Big Zero” a symbolic weight that extends far beyond its mechanical function, making it particularly appealing to collectors interested in the cultural and historical narratives embedded in objects. It is a watch that, literally and figuratively, marked a fresh start.
The Mikhail Gorbachev Anecdote and “Perestroika”: Analysing the Legend and Its Impact on Popularity
The Raketa “Big Zero” gained considerable international fame due to an anecdote involving Mikhail Gorbachev, the General Secretary of the USSR. During an official visit to Italy in the 1980s , when asked to explain the meaning of “Perestroika” (restructuring), Gorbachev reportedly pointed to his Raketa Big Zero watch and stated: “It’s like my watch: the Soviet people aspire to start everything from zero” or “It expresses the Russians’ determination to start their lives from ‘zero'”. This direct gesture made headlines in Italy and cemented the watch’s status as a legendary design. Although the exact origin of the design predates Gorbachev’s use, the anecdote undeniably boosted its popularity.
The Gorbachev anecdote transformed the “Big Zero” from a functional timepiece into a cultural icon. This direct link to a central historical figure and a transformative political movement (“Perestroika”) significantly increased its collectability and market value. The story, regardless of its precise historical accuracy regarding the design’s intent, has become an integral part of the watch’s identity, demonstrating how historical narratives and public figures can profoundly influence the perception and desirability of consumer goods.
Historical Context of Perestroika and Glasnost and Their Influence on Soviet Design
Perestroika (restructuring) and Glasnost (openness) were Mikhail Gorbachev’s reforms aimed at revitalising the stagnant Soviet economy and increasing political openness. These reforms introduced elements of market economics, encouraged private enterprise, and reduced central planning, leading to greater political and cultural freedoms and increased access to Western ideas and consumer goods. However, they also led to economic challenges such as shortages and inflation. The “Big Zero” emerged during this period of significant societal transformation , symbolising the desire for a fresh start.
The “Big Zero” design, with its symbolism of “starting from zero”, perfectly encapsulated the spirit of Perestroika and Glasnost. This connection goes beyond a mere anecdote; it suggests that even consumer goods like watches could reflect the profound social and political changes underway in the USSR. The watch became a subtle yet powerful representation of a nation grappling with change and aspiring to a new beginning, making it a compelling artefact for understanding the late Soviet era.
III. Historical Models and Variants of the Raketa Big Zero (Soviet Era)
Distinctive Features: Details on Cases, Dials, and Hands
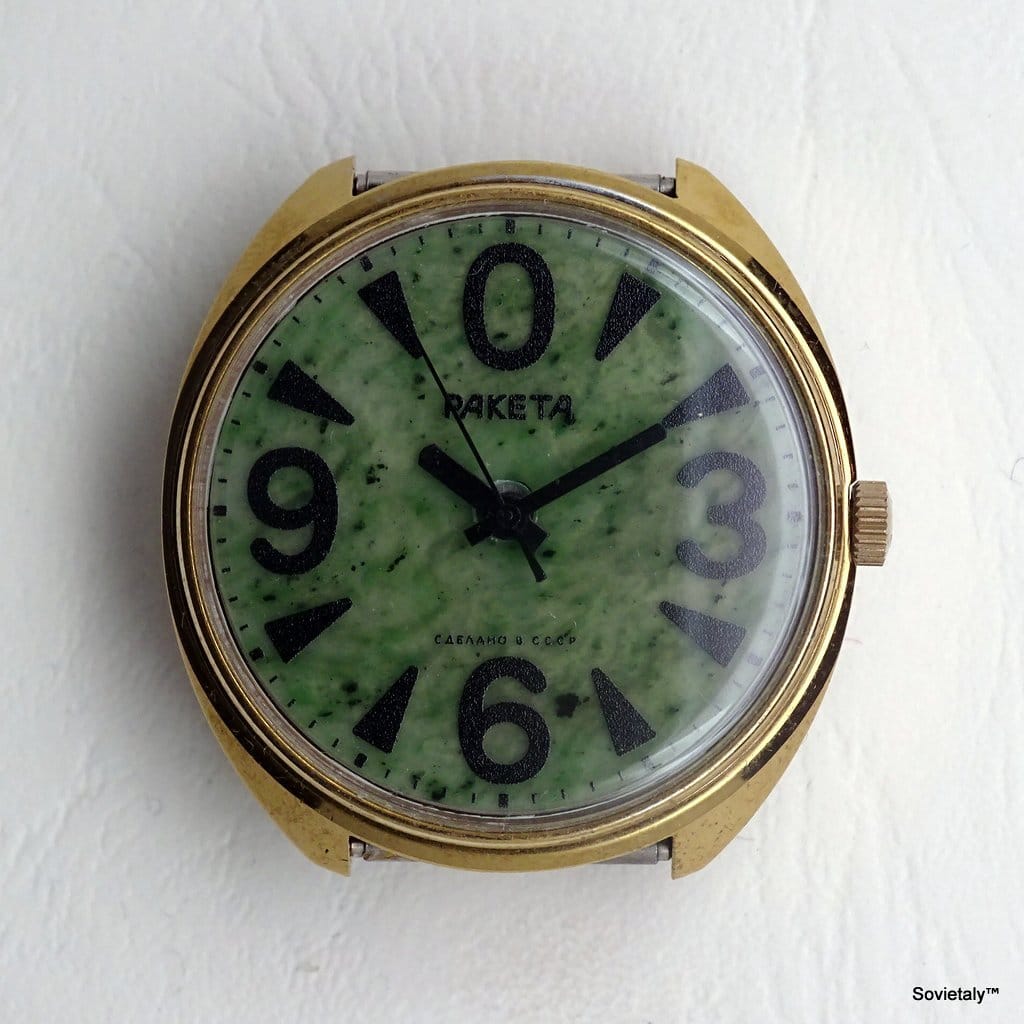
Vintage Raketa Big Zero watches are most commonly characterised by a cushion-shaped case, particularly reference #51. This case measures approximately 39mm in width (excluding crown), 40.5mm lug-to-lug, and 11mm in thickness. It features a smooth, press-on bezel with a slight bevel towards the crystal and a subtle upward curve in its profile when viewed from the side. The lugs are relatively small, which can sometimes make strap pairing challenging. Some vintage models were also available with a barrel-shaped stainless steel case. The case material was often chrome-plated brass.
Dials are typically black and white, offering high contrast. The iconic “0” at 12 o’clock, along with the numerals 3, 6, and 9, are oversized. The remaining hour markers are generally represented by long, narrow triangles. A crucial aspect for authentication is that these numerals and triangles are applied markers, appearing as a type of glossy resin or thin metal, rather than simply being printed. The tips of these wedge-shaped markers should be slightly rounded in cushion-cased variants, although some authentic dials from 1980s catalogues may feature sharper tips. The “0” itself is often described as “squarish” rather than a perfect oval.
The hour and minute hands are characteristically thick and bold, often described as “stubby”, with a slight tip or curve at their ends. The seconds hand is thin but flares slightly at the back end. These specific shapes are important for authentication, as incorrect hands are a common sign of “franken-watches” (watches assembled from non-original parts).
Vintage Big Zeros typically featured a steeply-domed acrylic (plexiglass) crystal. An authentic Raketa Big Zero crystal is described as “hockey puck”-shaped, with sharp edges that angle up 90 degrees towards a flat surface. This contrasts with modern sapphire crystals.
The consistency of design elements in vintage Big Zero models, such as the specific case shapes (cushion/barrel), applied numerals with rounded tips , and distinctive hand shapes , suggests a standardised production process within the Soviet system. The use of acrylic crystals instead of sapphire (common in modern versions) indicates the material availability and technological constraints of the era. However, this consistency also makes deviations from these norms critical indicators for identifying fakes or “franken-watches”, highlighting the importance of understanding original production specifications for collectors.
The 2609.HA Movement: Detailed Technical Specifications, Reputation for Reliability, and Common Issues
The Soviet-era Raketa Big Zero typically housed the mechanical hand-wound Calibre 2609.HA movement.
Technical Specifications:
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Calibre Name | Raketa 2609.HA |
| Type | Mechanical (Hand-Wound) |
| Launch Year | Circa 1975 |
| Jewels | 19 (some variants 17) |
| Frequency | 18,000 beats/hour (2.5 Hz) |
| Power Reserve | 45 hours (some sources indicate 36 hours or 24 hours ) |
| Functions | Hours, Minutes, Central Seconds |
| Shock Protection | Yes |
| Dimensions (Overall Diameter) | 26.65 mm |
| Height | 4.4 mm |
| Reputation | Reliable, Robust, Durable |
Reputation for Reliability: The 2609.HA movement is widely recognised for its durability and robustness. It is described as a “utilitarian, but very robust” movement that “can hold up to a lot”. It was even considered “the most reliable and robust movement in the world” in its time, with Russian watches exported to 38 countries. This reliability was a hallmark of Soviet watchmaking, which prioritised functionality and longevity over planned obsolescence.
Common Issues and Serviceability: While robust, vintage 2609.HA movements can exhibit issues due to age and lack of servicing. Common problems include low amplitude and inconsistent accuracy, especially when worn, which might indicate a loose hairspring. Setting issues, where the stem moves freely without interacting with the hands, can occur if the cannon pinion binds, causing minute wheel teeth to shear off. Repairs can be costly due to the need for non-standard parts. Servicing these movements requires specific techniques, particularly for delicate parts like the escape wheel jewels. Collectors are advised that antique watches are generally not waterproof and must be protected from moisture, and hands should only be adjusted clockwise to prevent damage.
The reputation of the 2609.HA calibre as a “robust” and “durable” movement is a direct consequence of Soviet-era production priorities. In a planned economy, the emphasis was on producing reliable, long-lasting goods for the masses and for critical state functions (military, exploration). This contrasts with market economies where planned obsolescence might be a factor. The common issues reported today (low amplitude, setting problems) are primarily age-related, not inherent design flaws, which underscores the movement’s fundamental durability. The difficulty in sourcing non-standard parts for repairs is a direct implication of the shift from a centralised production system to a global market, where parts for defunct Soviet industries are scarce.
Dial Variants and Markings: Analysing “Paketa” (Cyrillic) vs “Raketa” (English) and “Made in USSR” vs “Made in Russia” as Time and Market Indicators
The markings on the dial of vintage Raketa Big Zero watches provide crucial indicators for authentication and dating.
Logo: The brand logo can appear in two ways: “Paketa” (РАКЕТА in Cyrillic) or “Raketa” (in Latin characters). “Paketa” is characteristic of earlier Soviet-era models intended for the domestic market, while “Raketa” in Latin characters indicates more modern pieces or those produced closer to the collapse of the USSR (around 1992) for export.
Country Designation: Authentic Soviet-era dials typically feature “Сделано в CCCP” (Made in USSR in Cyrillic) for models intended for the domestic market or “Made in USSR” for export models. A red flag for authenticity is a dial with both “Paketa” (Cyrillic) and “Made in Russia” (English) simultaneously, or a dial with no country designation at all. Later (post-Soviet) models may bear “Сделано в России” or “Made in Russia”.
Quality Mark: Some vintage Big Zero models, particularly those from 1986 catalogues, might display the USSR state quality seal.
The variations in dial markings, such as Cyrillic “Paketa” versus Latin “Raketa”, and “Made in USSR” versus “Made in Russia” , serve as fundamental linguistic and historical markers. They reflect the Soviet Union’s evolving relationship with the global market and its subsequent dissolution. The shift to Latin script and “Made in Russia” signalling a post-Soviet era of increasing internationalisation and a move away from the more insular Soviet identity. For collectors, these subtle textual changes are vital for dating a watch and assessing its authenticity and market origin.
Special and Rare Editions
The Raketa Big Zero did not only exist in its most common form but also saw the production of various rare and special variants that add complexity and allure to its lineage.
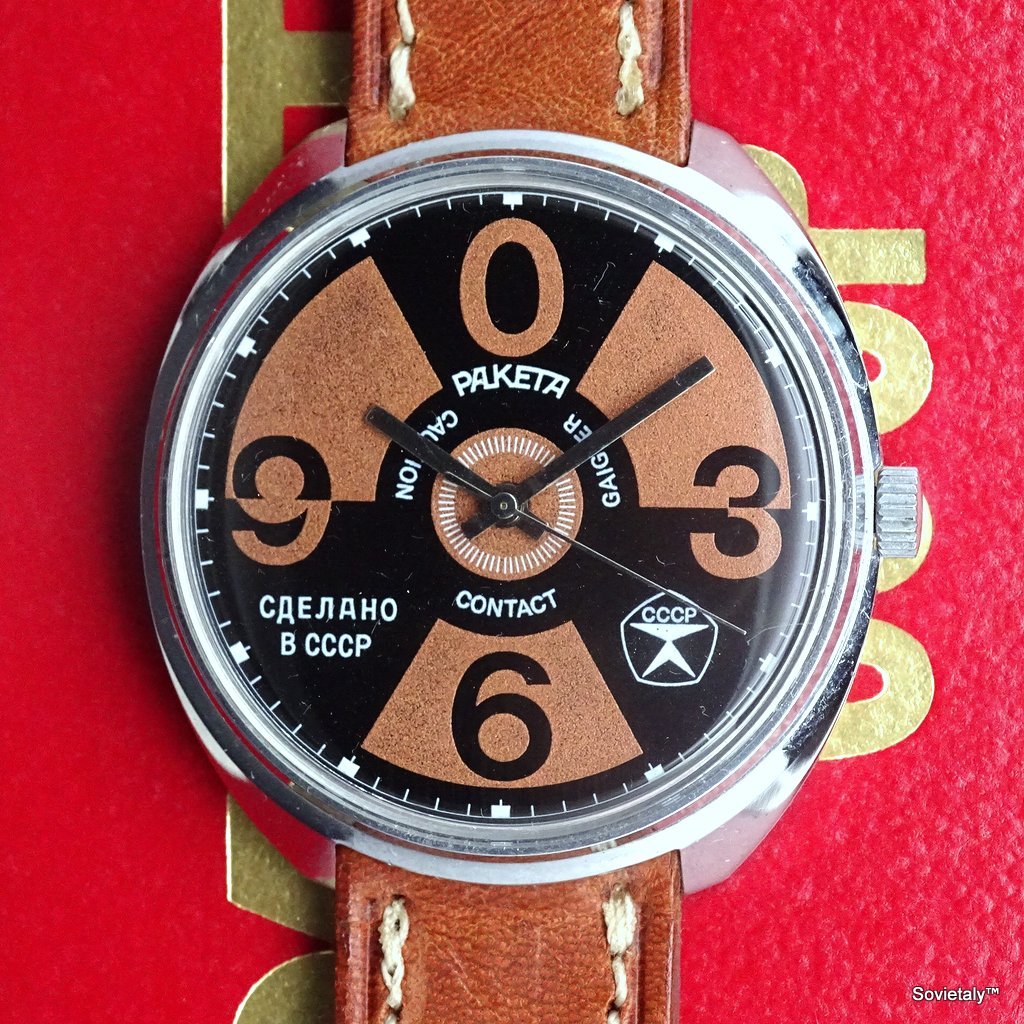
The “Big Zero Geiger”: This is a particularly unique and mysterious variant. It is said to have been assembled in Italy by an import company named “Mirabilia” in the late 1980s, using original Raketa Big Zero parts but adding a “unique local touch”. The most intriguing aspect is the intentional misspelling “Geigher” instead of “Geiger”. The theory suggests this was done to avoid negative associations with Geiger counters and radioactivity, especially after the Chernobyl incident in 1986, when public sensitivity to radioactivity was high. The Big Zero Geiger exists in two main variants: black and ochre, and black and grey. Both are extremely rare and highly sought after by collectors for their rarity, Soviet-Italian connection, and the mystery surrounding the name error.

Stone Dials (e.g., Jade) and Their Rarity: Raketa also produced Big Zero models with dials crafted from natural stone, such as jade. These dials, typically 0.5mm thick, boast unique and unrepeatable textures, making each watch a one-of-a-kind piece. They were produced in limited quantities, often by special order, and primarily intended for the Italian market. Cases for these models could be chrome-plated brass or titanium nitride (for yellow dials). These stone dial watches are now considered rare collectible items.

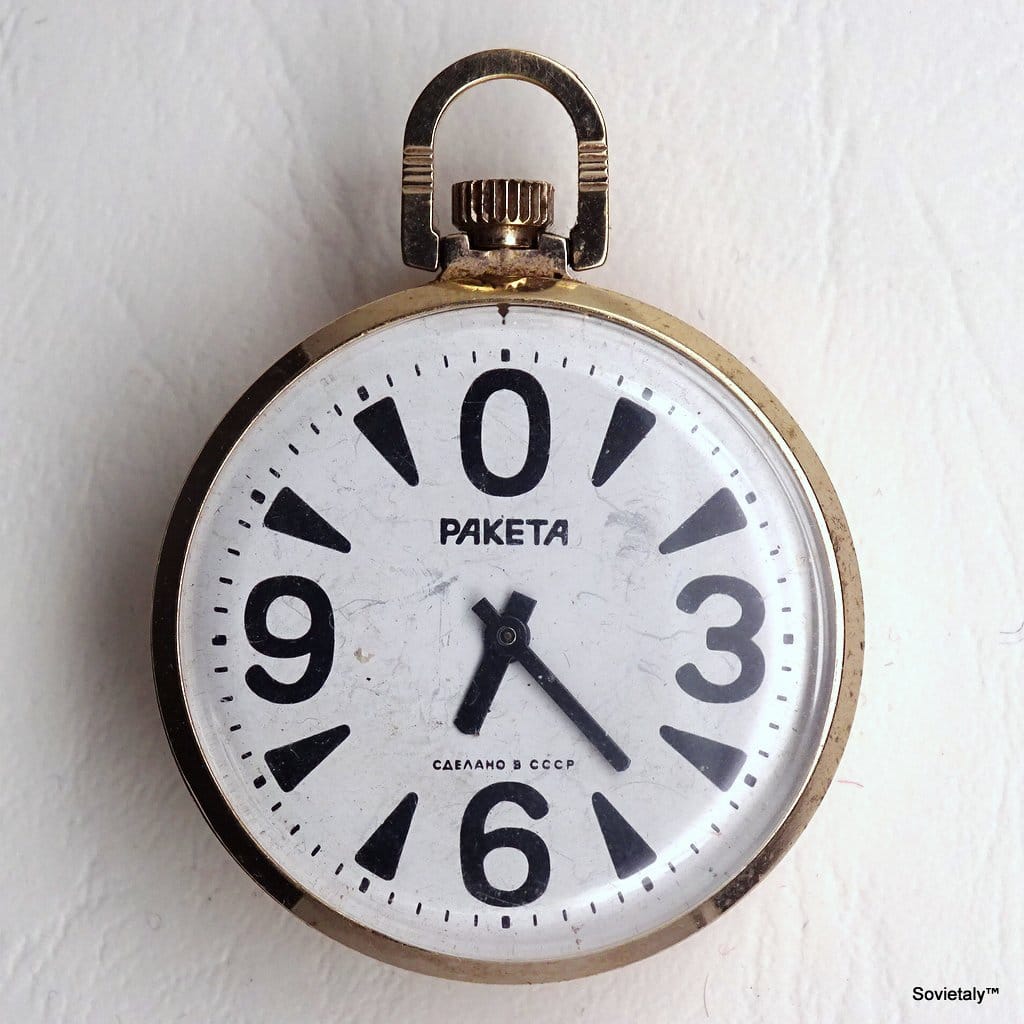
The Pocket Watch Version: A pocket watch variant matching the “Big Zero” design also existed, with catalogue images dating back to 1986. These “Big Zero” pocket watches typically feature a white dial with oversized black numerals and are powered by the Raketa 2609.HA hand-wound mechanical movement.

The existence of the “Big Zero Geiger” and the stone dial variants , particularly their Italian market orientation, reveals Raketa’s efforts to adapt to specific market demands and create niche products even during the Soviet era. The “Geigher” misspelling is a fascinating example of how external geopolitical events (Chernobyl) could directly influence product naming and marketing, highlighting a reactive and perhaps cautious approach to international sales. These rare variants demonstrate that Soviet production was not entirely monolithic and could respond to perceived market opportunities, adding layers of complexity to the brand’s history.
Raketa Pocket Watches: Finishes and Sailboat Engravings
In addition to wristwatches, Raketa also produced pocket watches with distinctive features. These pocket watches were generally powered by the Raketa 2609.HA hand-wound movement and featured typical dimensions of approximately 44mm overall diameter with the crown and 11.1mm thickness. Cases were often made of brass with chrome plating or, in some instances, gold-plated.
A notable aesthetic element on some Raketa pocket watches is the “caseback with a bas-relief in the form of a sailing ship”. This motif, variously described as “Raketa SHIP” or “Navy Brigantine” , was often paired with white dials featuring a matte surface and thin black Roman numerals, complemented by black, straight, thin hands. The sailboat likely symbolised Russia’s maritime heritage and naval power, given Raketa’s historical connection to the Soviet Navy and its location in Saint Petersburg.
It is important to note that while Raketa produced both “Big Zero” pocket watches and pocket watches with sailboat engravings , current research does not indicate the existence of an original factory Raketa “Big Zero” pocket watch that combines both features (a “Big Zero” dial and a sailboat engraving on the caseback). Descriptions of sailboat pocket watches consistently refer to dials with Roman numerals , suggesting these were distinct design lines. Therefore, a pocket watch claiming to combine a “Big Zero” dial with a sailboat engraving should be examined with extreme caution, as it may be a “frankenwatch” or a non-original assembly.
Table 1: Technical Specifications of the Raketa 2609.HA Movement
The following table provides a consolidated reference for the mechanical heart of vintage Big Zeros. For collectors, verifying movement specifications is crucial for authentication and understanding the watch’s performance characteristics. The inclusion of variations (e.g., 17 or 19 jewels, power reserve discrepancies) highlights the nuances of Soviet production and helps manage expectations regarding the performance of vintage pieces. It also serves as a direct comparison point for modern automatic movements, illustrating the Big Zero’s technical evolution.
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Calibre Name | Raketa 2609.HA |
| Type | Mechanical (Hand-Wound) |
| Launch Year | Circa 1975 |
| Jewels | 19 (some variants 17) |
| Frequency | 18,000 beats/hour (2.5 Hz) |
| Power Reserve | 45 hours (Note: some sources indicate 36 hours or 24 hours ) |
| Functions | Hours, Minutes, Central Seconds |
| Shock Protection | Yes |
| Dimensions (Overall Diameter) | 26.65 mm |
| Height | 4.4 mm |
| Reputation | Reliable, Robust, Durable |
Table 2: Historical Dial Variants and Markings of the Big Zero
This table is an essential authentication tool. It systematically categorises key visual cues on the dial, hands, and case that distinguish authentic vintage Big Zeros from fakes or “franken-watches”. By presenting these variations and their implications (e.g., time indicators, market origin), it empowers collectors to make informed purchasing decisions and appreciate the subtle historical evolution of the watch’s aesthetic.
| Feature | Authentic Characteristics | Implications | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dial Logo | “Paketa” (РАКЕТА in Cyrillic) or “Raketa” (Latin) | Cyrillic for earlier domestic Soviet market; Latin for later Soviet or export models | Mix of Cyrillic logo and “Made in Russia” (English) |
| Country Designation | “Сделано в CCCP” (Cyrillic) or “Made in USSR” (English) | Cyrillic for domestic Soviet market; English for export models. “Made in Russia” for post-Soviet era | No country designation; Mix of Cyrillic logo and “Made in Russia” (English) |
| Hour Marker Shape (Triangles) | Rounded tips (for cushion case); some 1980s catalogues show sharper tips | Key detail for cushion-cased model authentication | Pointy/sharp tips on cushion-cased models |
| Numeral Application | Applied markers (glossy resin or thin metal, slightly raised) | Indicates higher quality and original production | Flat/printed numerals |
| Hands | Thick, bold, “stubby” hour/minute hands with slight tip/curve; thin seconds hand with slight flare at back | Specific proportions and shapes are crucial for originality | Hands with incorrect shapes or proportions |
| Crystal | Acrylic, “hockey puck” shape (sharp 90-degree edges towards flat top) | Reflects original Soviet-era materials | Domed or overly rounded crystal |
IV. The Raketa Big Zero in the Modern Era: Continuity and Innovation
The Contemporary Re-edition of the Big Zero: Models 0283 (White), 0296 (Black), 0297 (Grey), and the “Arabic” Edition
Raketa has successfully re-issued the iconic Big Zero in contemporary collections, maintaining its distinctive design while incorporating modern materials and movements.
Current Models:
- Big Zero 0283 (White): Features a matte white dial with multi-layered lacquered black numerals and indices, paired with a black leather strap. It was launched in 2022.
- Big Zero 0296 (Black): A black dial variant with white numerals, launched in late 2023, featuring highly luminescent numerals and indices.
- Big Zero 0297 (Grey): Introduced for the first time with a stainless steel bracelet, it features a grey dial that changes shade from taupe to metallic depending on the light. It also boasts bright Superluminova-coated hands and large numerals for optimal night readability. This was a limited production of 200 pieces in its launch year.
- Big Zero Arabic: Reimagined specifically for the Middle East, this limited edition (initially 100 pieces) features Eastern Arabic numerals on a black and white dial, with the Raketa logo in Arabic script designed by renowned calligrapher Mohammad Sharaf. This collaboration reflects a growing interest in foreign watch brands in the Middle East and Raketa’s strategy to combine Russian watchmaking history with regional cultural elements.
Common Technical Specifications (Modern Models):
- Movement: Raketa 2615 in-house automatic calibre.
- Jewels: 24 jewels (some sources indicate 27, potentially an earlier variant of the 2615).
- Frequency: 18,000 beats/hour (2.5 Hz).
- Power Reserve: 40 hours.
- Winding: Bi-directional automatic winding with a stopper system for manual winding.
- Accuracy: -10/+20 seconds per day.
- Decoration: Laser engraving, Neva waves, and often a red rotor visible through the transparent caseback.
- Material Origin: All metal and the 24 ruby stones of the movement come from Russia, with the hairspring cast from a secret Soviet alloy, contributing to a distinctive acoustic signature.
- Case: Stainless steel, cushion shape, 40mm diameter, 14.05mm thickness, 43mm lug-to-lug. Crown with a ruby stone underneath.
- Crystal: Sapphire on the front, mineral on the transparent caseback.
- Water Resistance: 10 ATM / 100 metres.
- Luminosity: Hands and indices with Superluminova coating.
The modern re-editions of the Big Zero (0283, 0296, 0297, Arabic) demonstrate Raketa’s successful strategy in modernising its brand while retaining its fundamental design identity. The shift from the hand-wound 2609.HA movement to the automatic 2615 movement , the upgrade to sapphire crystal, and increased water resistance reflect contemporary market expectations for luxury watches. However, the retention of the iconic “Big Zero” dial and the commitment to in-house movement production (even with Russian materials) highlight a deliberate effort to maintain authenticity and appeal to both new and traditional collectors. The limited editions and regional variants (like the Arabic dial) further showcase a sophisticated marketing approach to cater to diverse global markets.
Comparison Between Vintage and Modern Models: Technical and Philosophical Evolution
The comparison between vintage and modern Raketa Big Zero models reveals a significant evolution both technically and philosophically, while maintaining a strong connection to the original design identity.
Movement: The most significant transition is the shift from the hand-wound 2609.HA calibre (vintage) to the automatic 2615 calibre (modern). While the 2609.HA was known for its robustness and simplicity in an era of mass production , the 2615 offers the convenience of automatic winding, a 40-hour power reserve, and more elaborate decoration visible through the transparent caseback.
Materials and Finishes: Modern models utilise stainless steel for the case and sapphire crystal for the front, enhancing durability and scratch resistance compared to the chrome-plated brass and acrylic crystal of vintage pieces. The addition of a ruby in the crown on modern models adds a touch of luxury.
Water Resistance: Vintage models were generally not waterproof , whereas modern ones offer 10 ATM / 100 metres of resistance, making them suitable for daily wear and light swimming.
Design Philosophy: Although the iconic “Big Zero” design remains faithful to the original, the transition from a functional, mass-produced Soviet-era watch to a collectible, luxury piece in the modern era is evident. Modern models are positioned for an audience that appreciates both history and in-house craftsmanship, with an average price point of around €1,200. The limited production of some modern editions (e.g., 200 pieces for the grey, 100 for the Arabic) underscores their exclusivity.
The comparison reveals a clear evolution from a utilitarian, mass-produced item (the vintage Big Zero) to a collectible luxury item (the modern Big Zero). This transformation is driven by technological advancements (automatic movement, sapphire, water resistance) and a strategic brand repositioning in a global market. The modern Raketa leverages its historical authenticity and in-house production capabilities to justify a higher price point and attract discerning collectors. This shift reflects broader trends in the watch industry, where historical brands adapt to new consumer expectations while preserving their unique heritage.
Table 3: Comparison Between Vintage and Modern Raketa Big Zero Models
The following table offers a concise and direct comparison highlighting the key differences and improvements between vintage and modern Big Zero models. It helps readers quickly grasp the watch’s evolution and provides practical information for collectors interested in both eras. It also reinforces the narrative of modernisation while preserving heritage.
| Feature | Vintage Models | Modern Models |
|---|---|---|
| Era | Soviet (1970s – early 1990s) | Post-Soviet (Revival from 2010 onwards) |
| Movement | Calibre 2609.HA (Hand-Wound) | Calibre 2615 (Automatic, In-House) |
| Case Material | Chrome-plated Brass | Stainless Steel |
| Crystal Material | Acrylic (Plexiglass) | Sapphire (Front), Mineral (Caseback) |
| Water Resistance | Generally Not Waterproof | 10 ATM / 100 Metres |
| Dial Numerals/Indices | Applied, triangle tips typically rounded (cushion case) | Multi-layered lacquered, Superluminova coating |
| Approximate Price Range | $80 – $400+ (depending on condition, rarity, “franken” status) | €1,200 – €2,200+ (based on models like 0283, 0297, Amphibia) |
V. Authentication and Collecting Guide
Identifying Fakes and “Franken-watches”: Red Flags on Dials, Hands, Cases, and Movements
The market for vintage Soviet watches, including the Raketa Big Zero, contains a significant number of fakes and “franken-watches” (pieces assembled from non-original parts). Collectors must be vigilant.
Dials: This is the most commonly faked component.
- Marker Shape: Authentic Big Zeros (especially cushion-cased ones) feature triangular hour markers with slightly rounded tips. Fakes often have pointy or sharp wedges. However, some authentic 1980s catalogues show sharper tips, so this is not a definitive standalone criterion.
- Numeral Shape: The “0” and other numerals (3, 6, 9) should appear “squarish” rather than perfectly oval, with subtle variations in thickness.
- Application: Authentic numerals and triangles are applied markers (glossy resin or thin metal, slightly raised), not simply flat printed. Flat printing is a major red flag.
- Print Quality: Fakes often exhibit poor print quality, with “hairy” or uneven edges on the numerals.
- Logo and Country Designation:
- “Paketa” (Cyrillic) is for the domestic Soviet market; “Raketa” (Latin) for later Soviet or export models.
- Authentic country designations are “Сделано в CCCP” (Cyrillic) or “Made in USSR” (English).
- A mix of Cyrillic logo and “Made in Russia” (English) on the same dial, or the absence of any country designation, are strong red flags.
Hands: Incorrect hands are a common issue for “franken-watches”. Authentic hour and minute hands are thick and “stubby” with a slight tip/curve, while the seconds hand is thin but flares slightly at the back. Deviations from these specific shapes are warning signs.
Cases: The authentic Big Zero (cushion) case features a smooth, press-on bezel with a slight bevel and a continuous curve from the case midpoint to the lug tips. Many “franken-watches” feature incorrect case shapes or lugs. Vintage cases were often chrome-plated brass, which may show signs of wear over time.
Crystal: An authentic vintage Big Zero crystal is acrylic and “hockey puck”-shaped (sharp 90-degree edges towards a flat top), not a dome.
Pocket Watches: For pocket watches, it is crucial to verify the consistency between the dial and the caseback. While Raketa “Big Zero” pocket watches exist and Raketa pocket watches with sailboat engravings (typically with Roman numeral dials) are also found, the combination of a “Big Zero” dial with a sailboat caseback is not documented as original factory production. Therefore, a pocket watch exhibiting both these features should be considered a “frankenwatch” or a non-original assembly.
Movement: While the 2609.HA is robust, it is important to ensure it is the correct movement for the model. Some 24-hour dials might be paired with a 2609.HA, which makes the watch a “fake” for a 24-hour watch, unless it is a third-party conversion.
The proliferation of fakes and “franken-watches” in the Soviet watch market is a direct consequence of their increasing popularity and affordability. The detailed authentication points (dial markings, hand shapes, case contours) become critical tools for collectors. This situation reflects the challenges of collecting items from a defunct political-economic system, where original documentation might be scarce and parts supply irregular, creating a fertile ground for deceptive practices. Understanding these nuances is essential to preserving the historical integrity of a collection.
Advice for Collectors: What to Look For, Where to Buy, Importance of Condition and Documentation
For collectors interested in the Raketa Big Zero, it is crucial to adopt an informed approach to ensure the authenticity and value of acquired pieces.
Authenticity: Always verify authenticity by checking for matching serial numbers, correct caseback engravings, and original dials. Be wary of overly polished or altered pieces.
Condition: While patina can add character, watches with minimal modifications and original parts are more desirable. Overly restored or repainted dials can diminish collectability.
Where to Buy: Online platforms like eBay and Chrono24 are common sources, but caution is advised due to the presence of fakes. Reputable Russian watch forums (e.g., the Russian Watch Forum on Watchuseek.com) are excellent resources for information and advice from the community. Direct purchases from official Raketa stores (physical or online) guarantee authenticity for modern models.
Pricing: Vintage Big Zero wristwatches can range from under $105 to over $160, with some rare variants fetching higher prices (e.g., “Big Zero” Peterhof CCCP full set NOS at $370, or “Salmon Dial” at $416). Raketa pocket watches with sailboat engravings can be found in the range of approximately $55-$70 , while Raketa “Big Zero” pocket watches are priced between approximately $89 and $176. Modern re-editions are significantly higher priced, around €1,200 – €2,200. The value of Soviet watches is increasing due to their historical depth, unique appeal, and the growing scarcity of well-preserved pieces.
Serviceability: It is important to be aware that vintage mechanical watches often require servicing. While the 2609.HA is robust, repairs can be costly due to non-standard parts. It is advisable to seek out competent hobbyists or specialised watchmakers for maintenance.
The advice for collectors, including authenticity checks, condition assessment, and seeking reliable sources, highlights the evolving nature of the Soviet watch market. What was once a niche, affordable segment is gaining increasing attention, leading to rising values and a greater presence of fakes. The community aspect, through forums, plays a crucial role in knowledge sharing and combating fraud. This market dynamic underscores the transformation of Soviet watches from mere utilitarian objects to highly sought-after historical artefacts, whose value is increasingly tied to their verifiable originality and historical narrative.
Conclusions
The Raketa Big Zero stands as a compelling testament to Soviet horological ingenuity and design philosophy. Its journey from a functional timepiece born in the 1970s to a global cultural icon, deeply intertwined with the Perestroika era, underscores its unique historical significance. The original design, prioritising legibility and practicality, has resonated through the decades, influencing both vintage collecting and modern re-editions.
The enduring legacy of the Petrodvorets Watch Factory, from its imperial founding to its commitment to in-house movement production today, provides a robust foundation for the Raketa brand’s authenticity. The technical robustness of movements like the 2609.HA in vintage models, contrasted with the modernised automatic 2615 in contemporary versions, showcases a brand that respects its heritage while embracing innovation.
For collectors, the Raketa Big Zero offers a rich and rewarding pursuit, though it demands careful attention to authentication details. The proliferation of “franken-watches” necessitates a thorough understanding of historical dial markings, hand shapes, and case characteristics, including the distinction between wristwatch and pocket watch variants. Awareness that “Big Zero” pocket watches and those with sailboat engravings are separate design lines is crucial to avoid non-authentic pieces. The market’s appreciation for these watches continues to grow, driven by their unique blend of history, design, and mechanical integrity.
Ultimately, the Raketa Big Zero is more than a time-telling device; it is a tangible narrative of Russian history, technological ambition, and societal change, making it a truly distinctive piece in the world of horology.