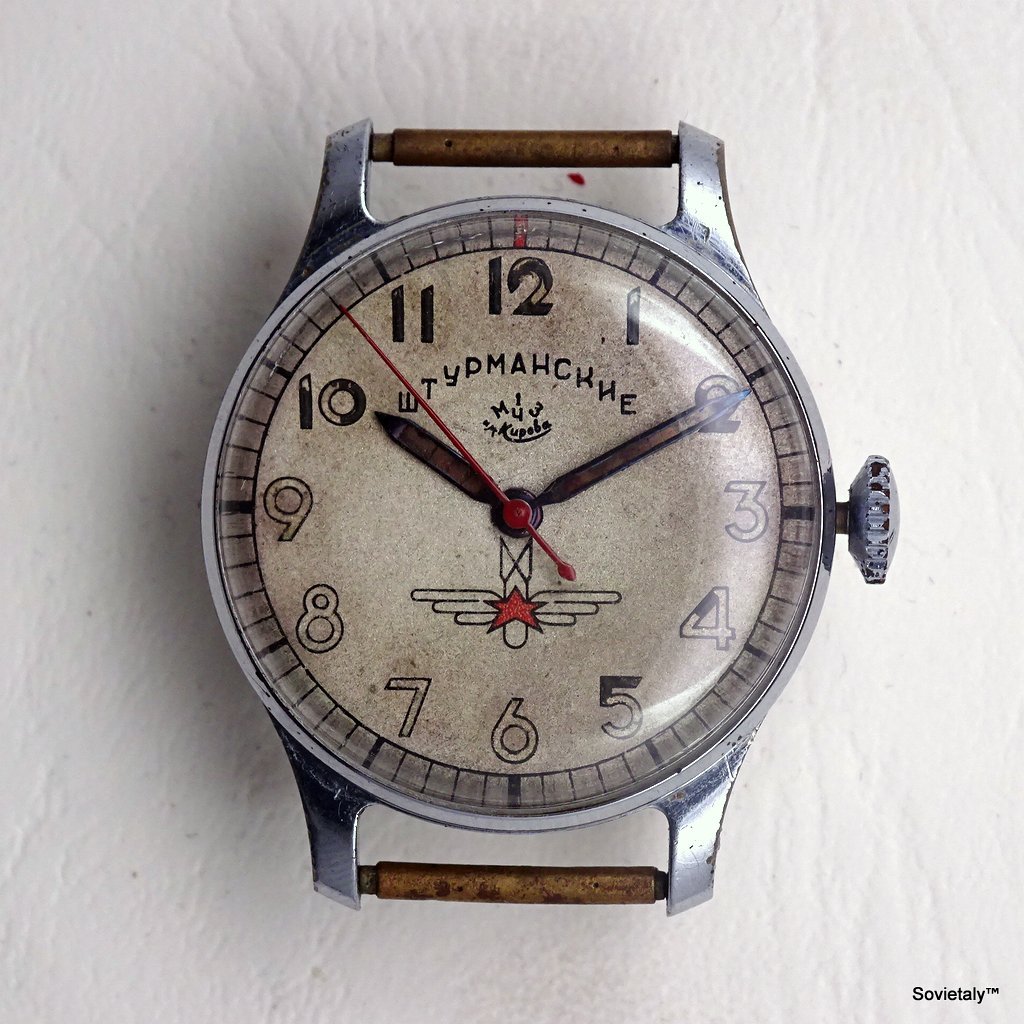
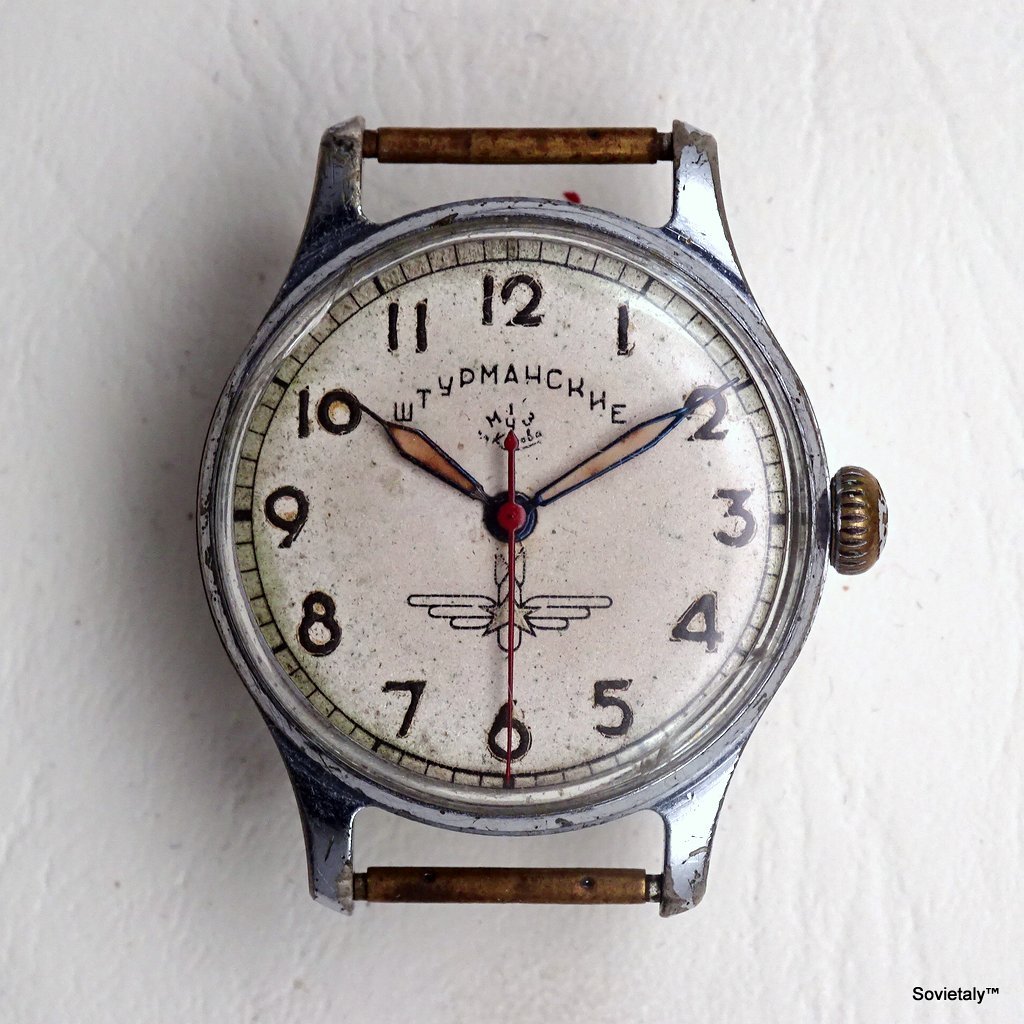
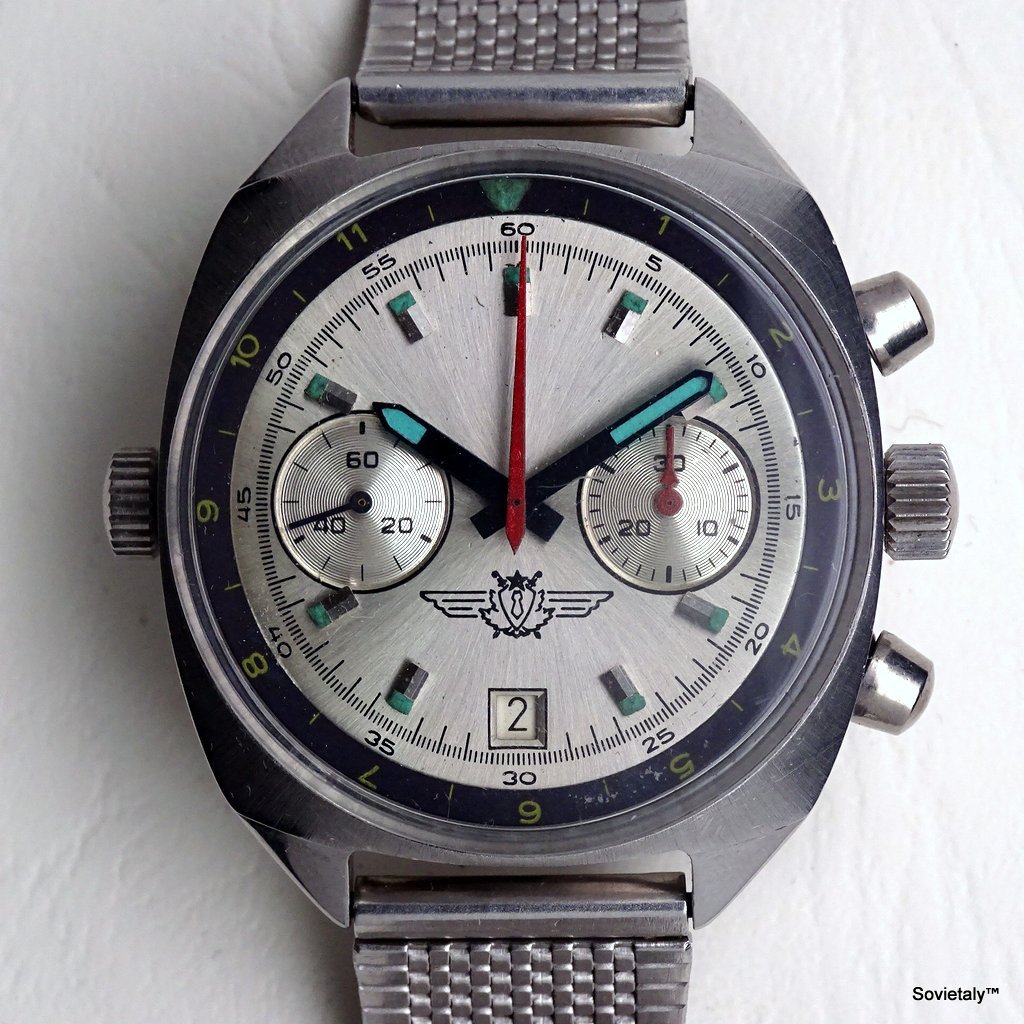
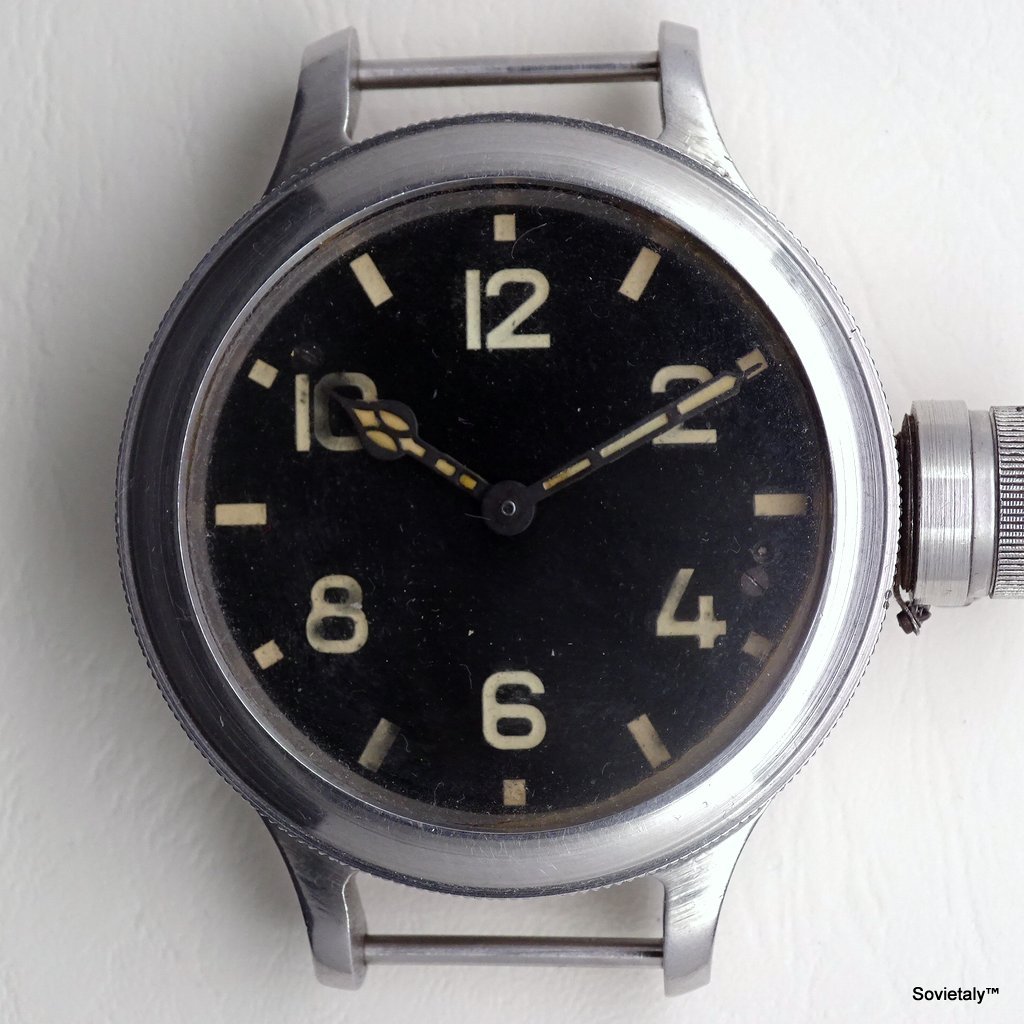
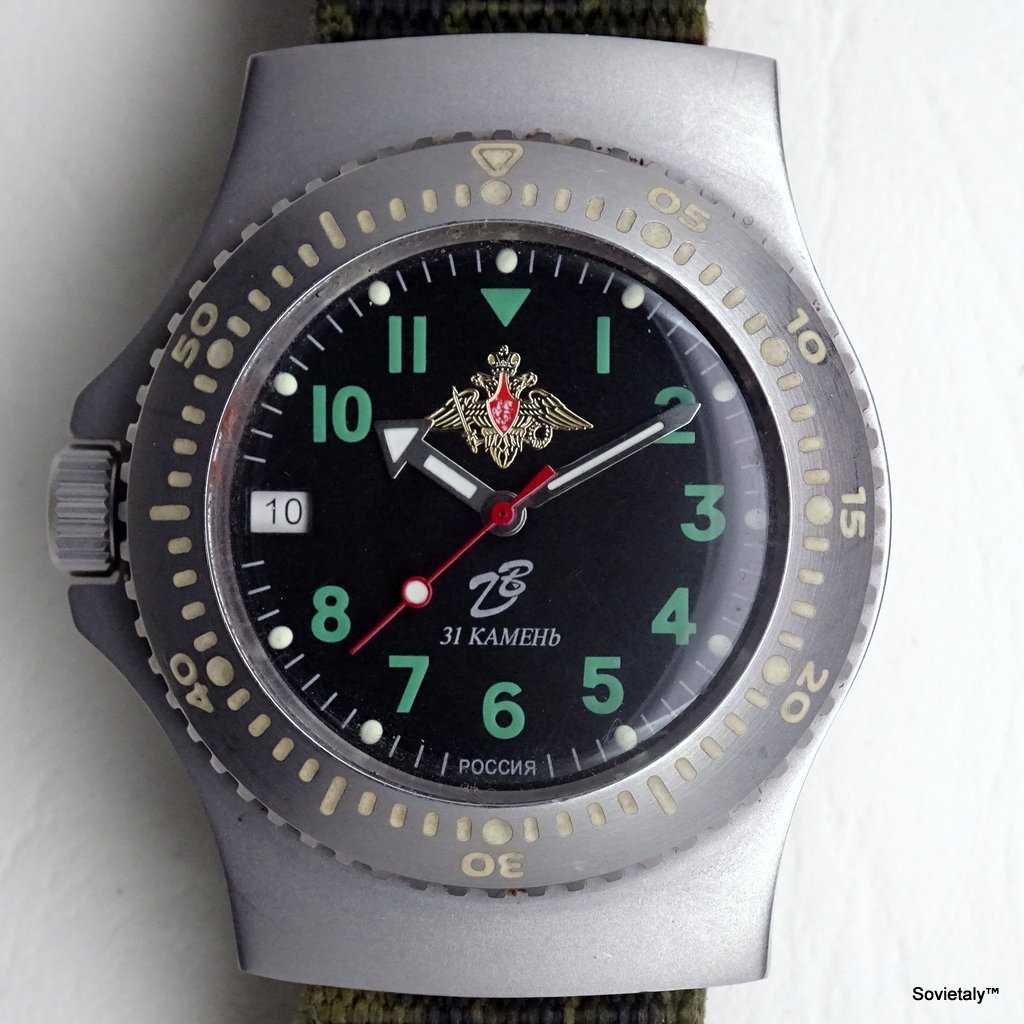
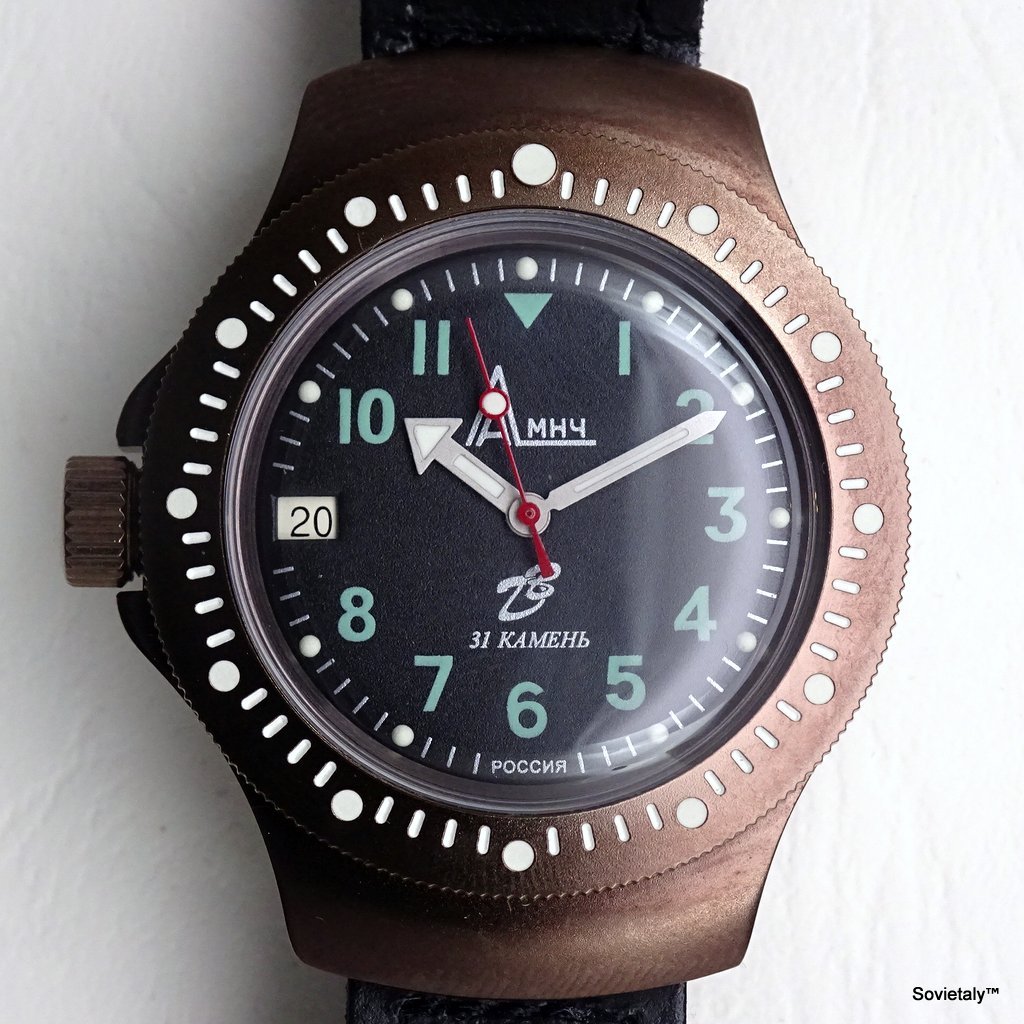
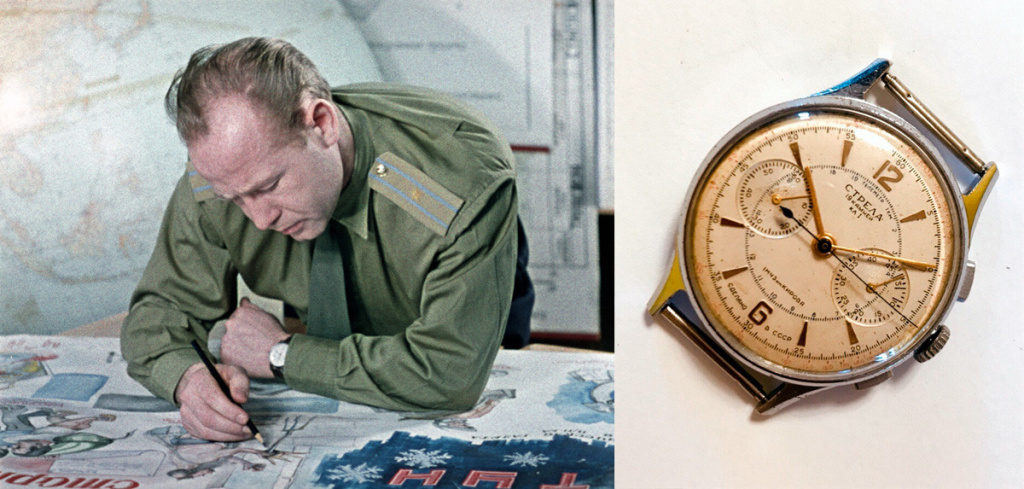
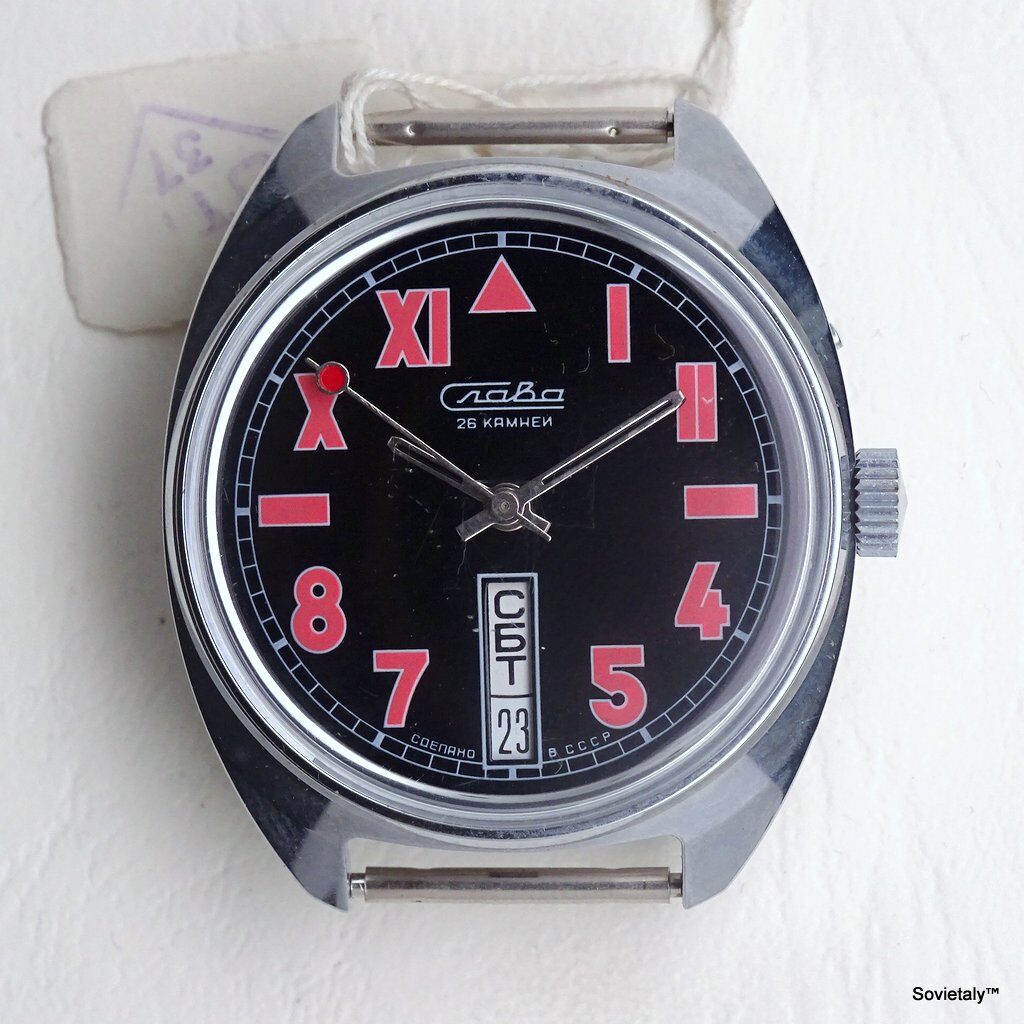
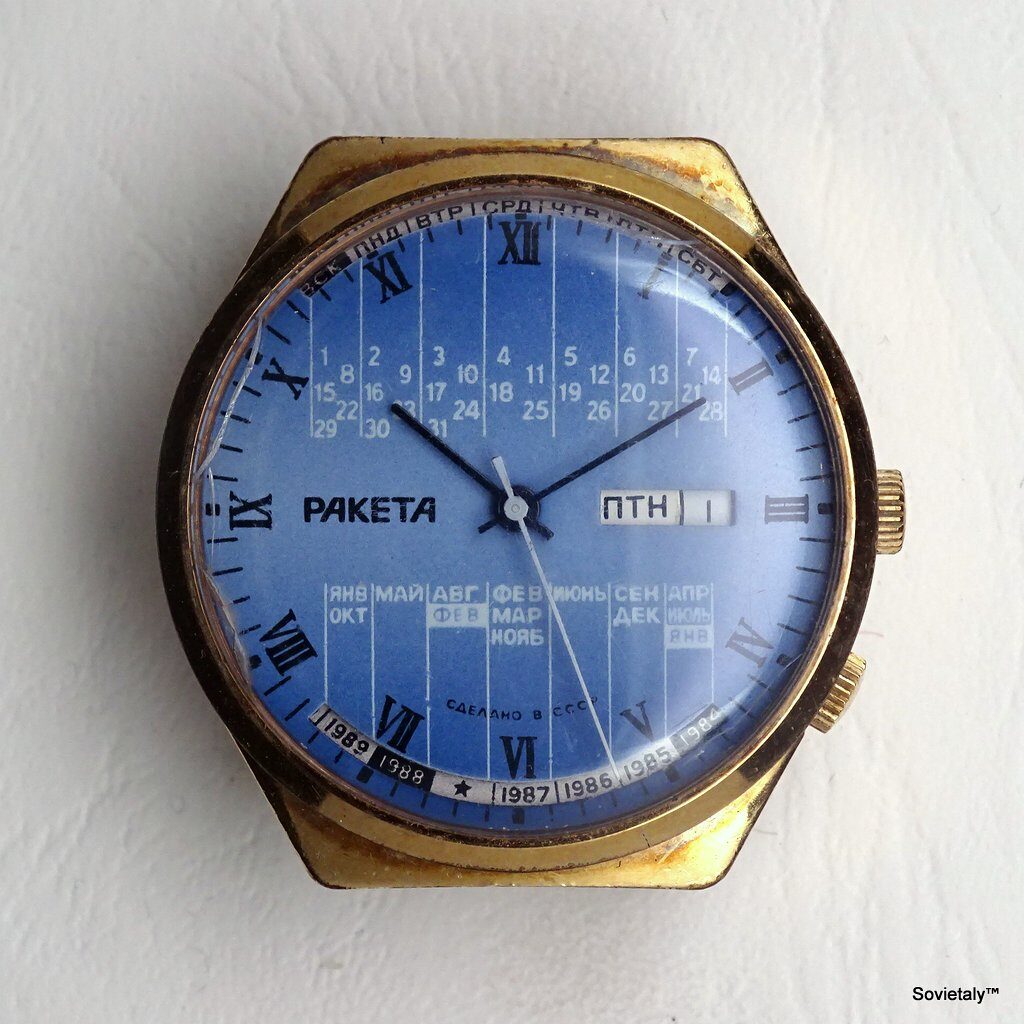
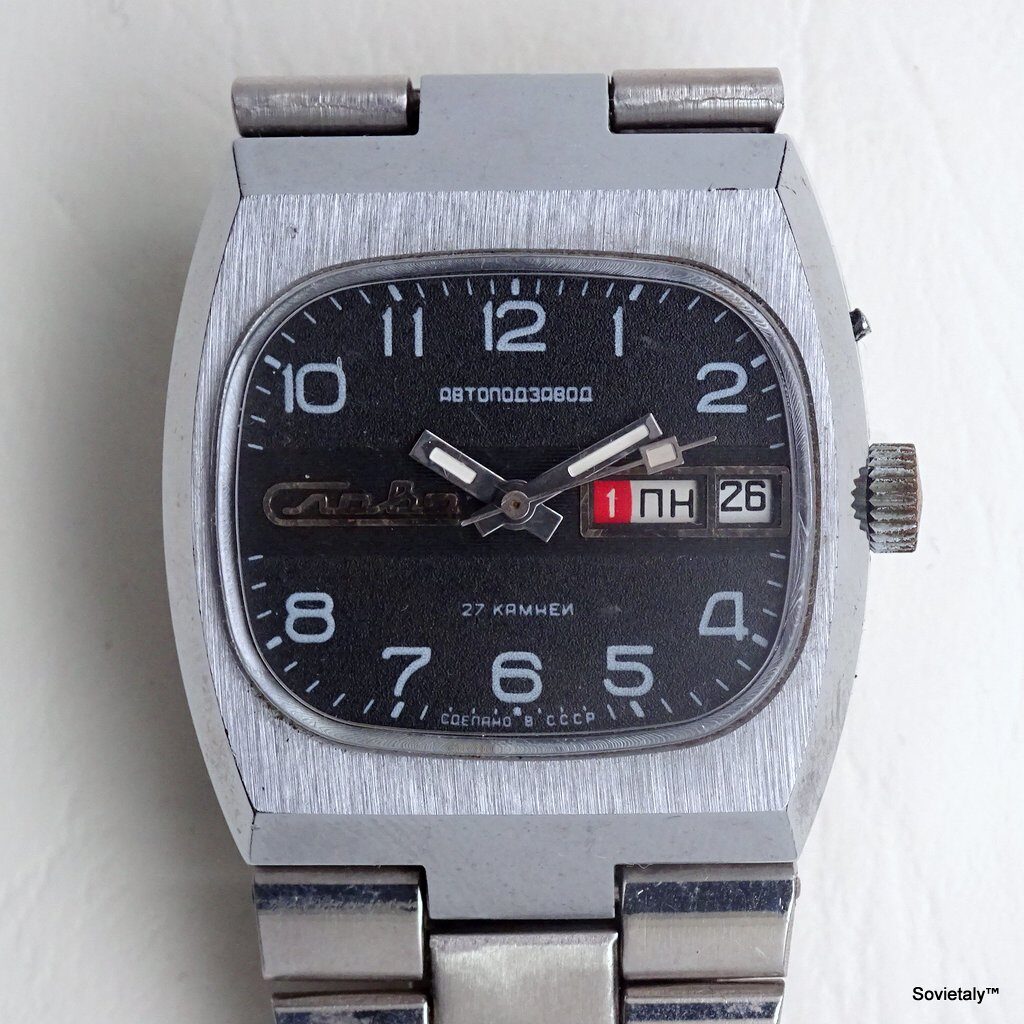
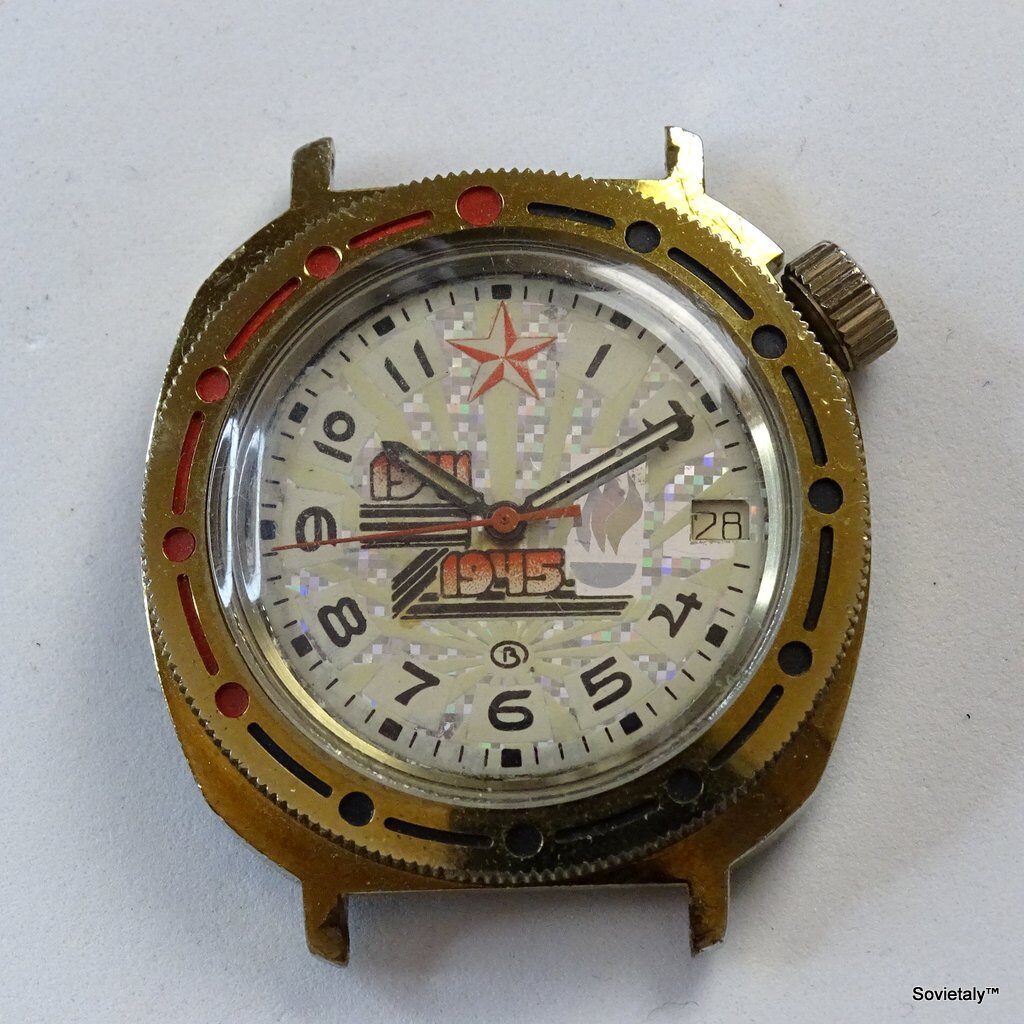
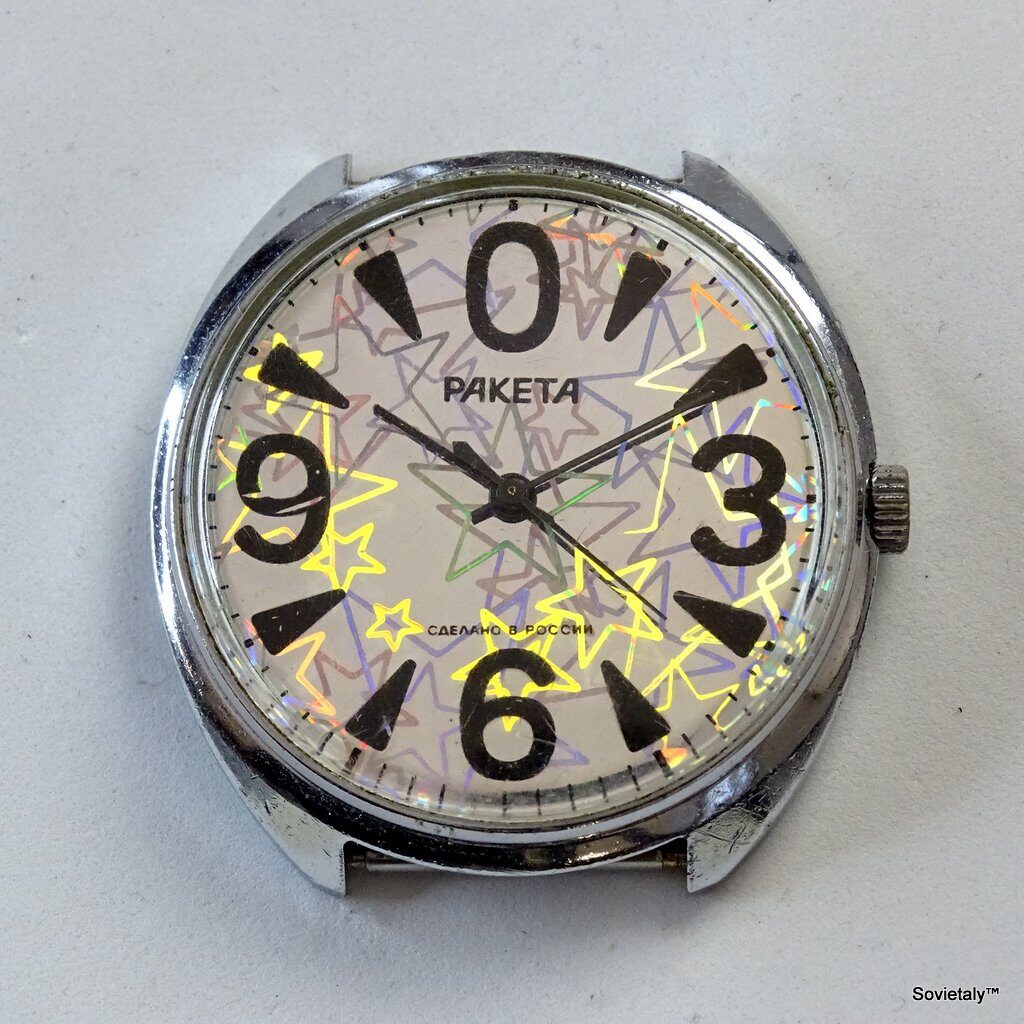
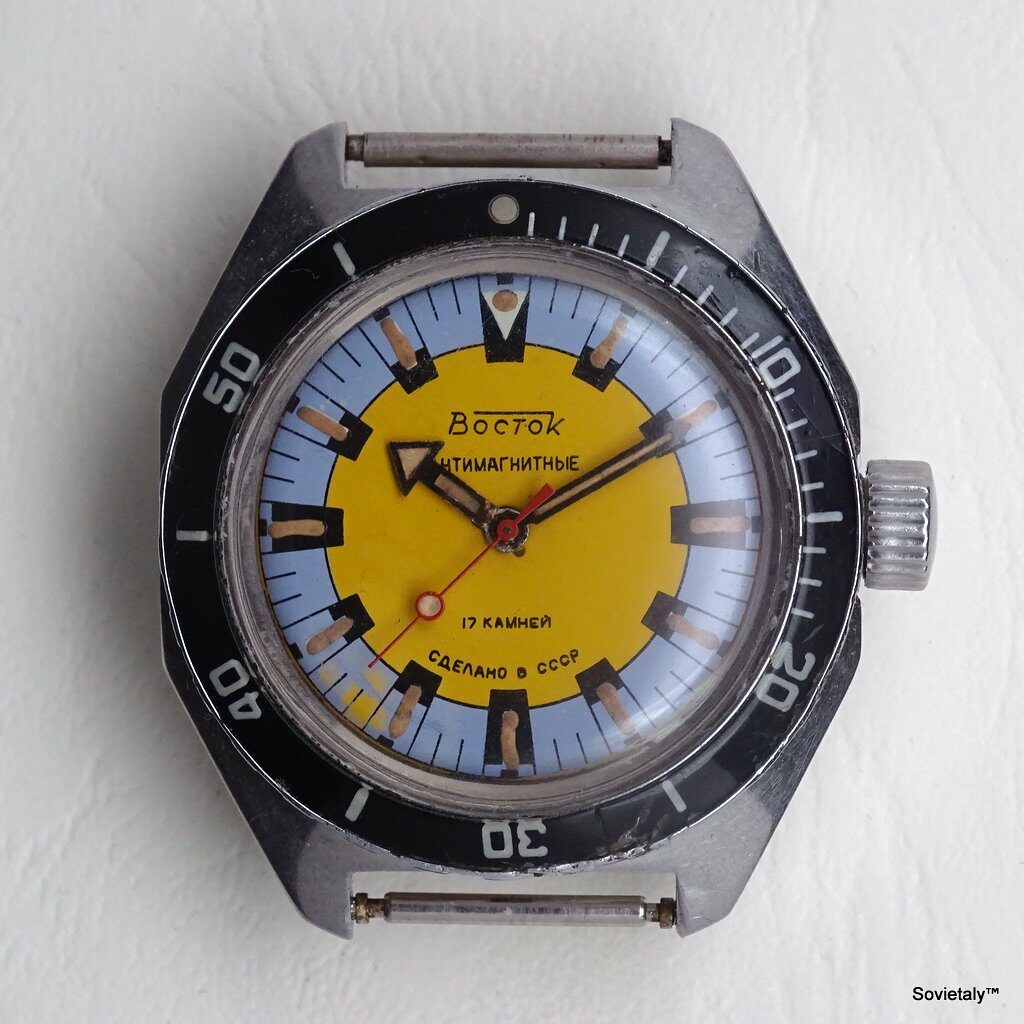
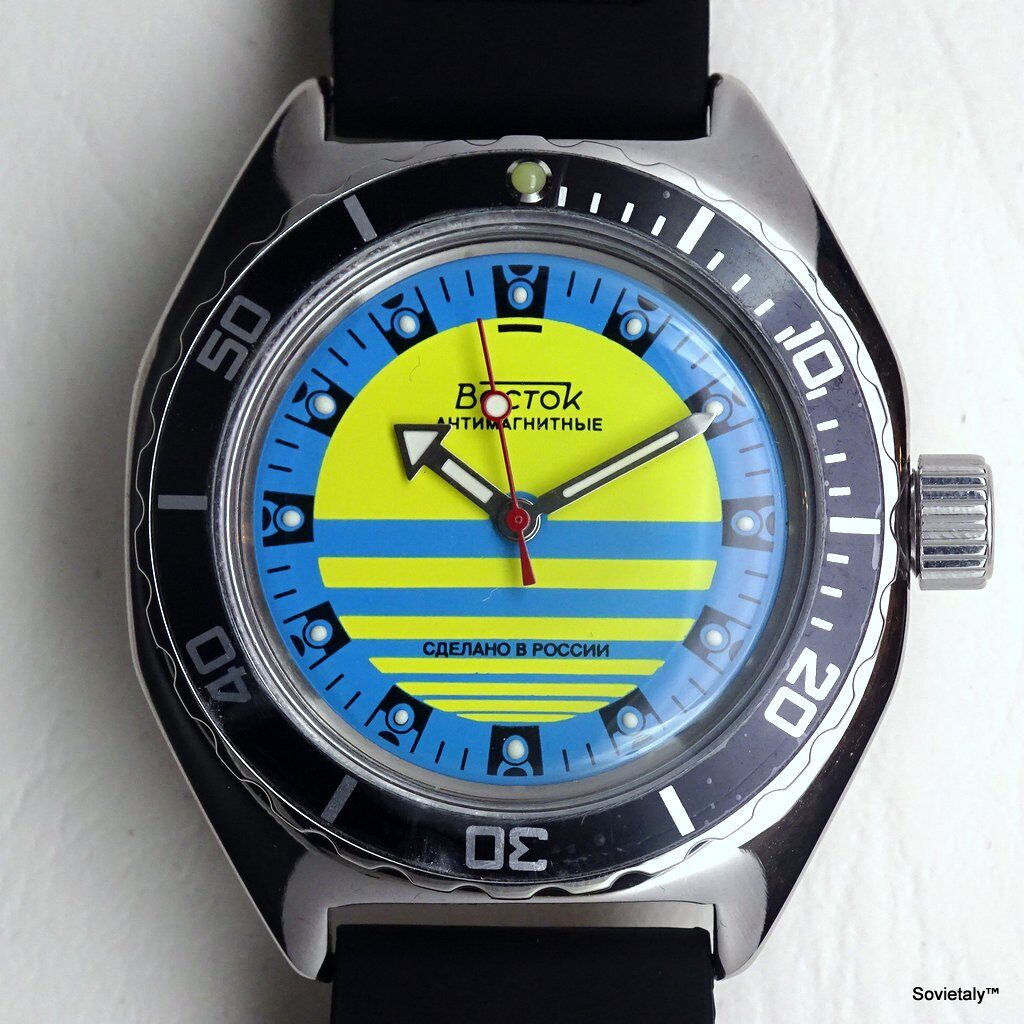
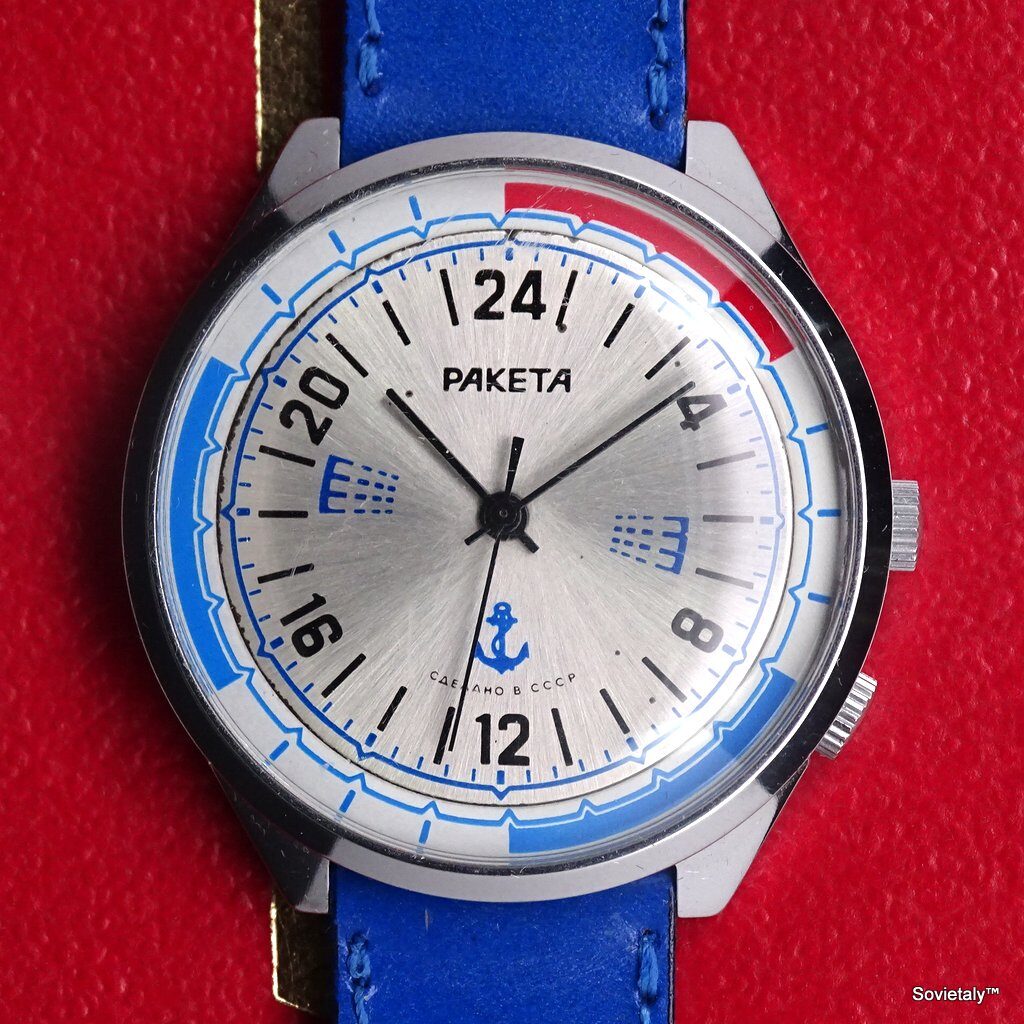
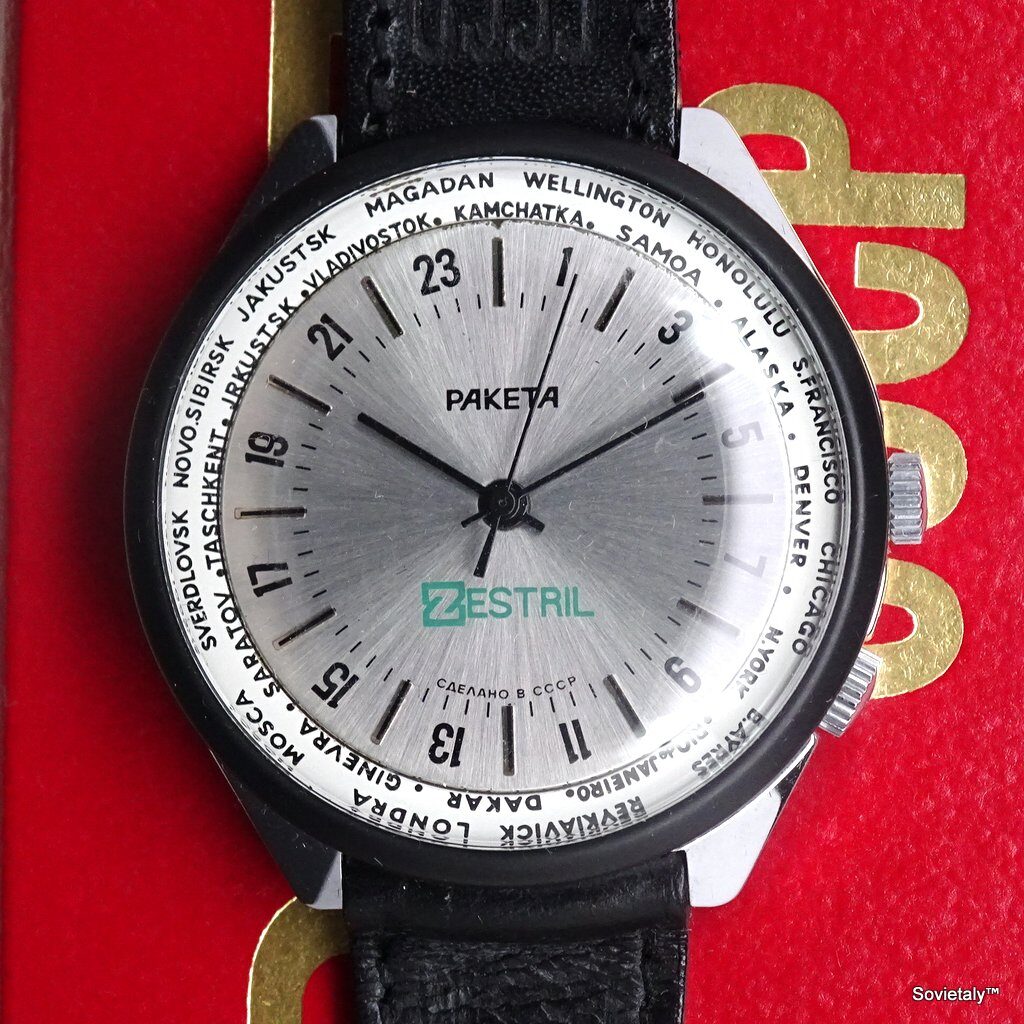
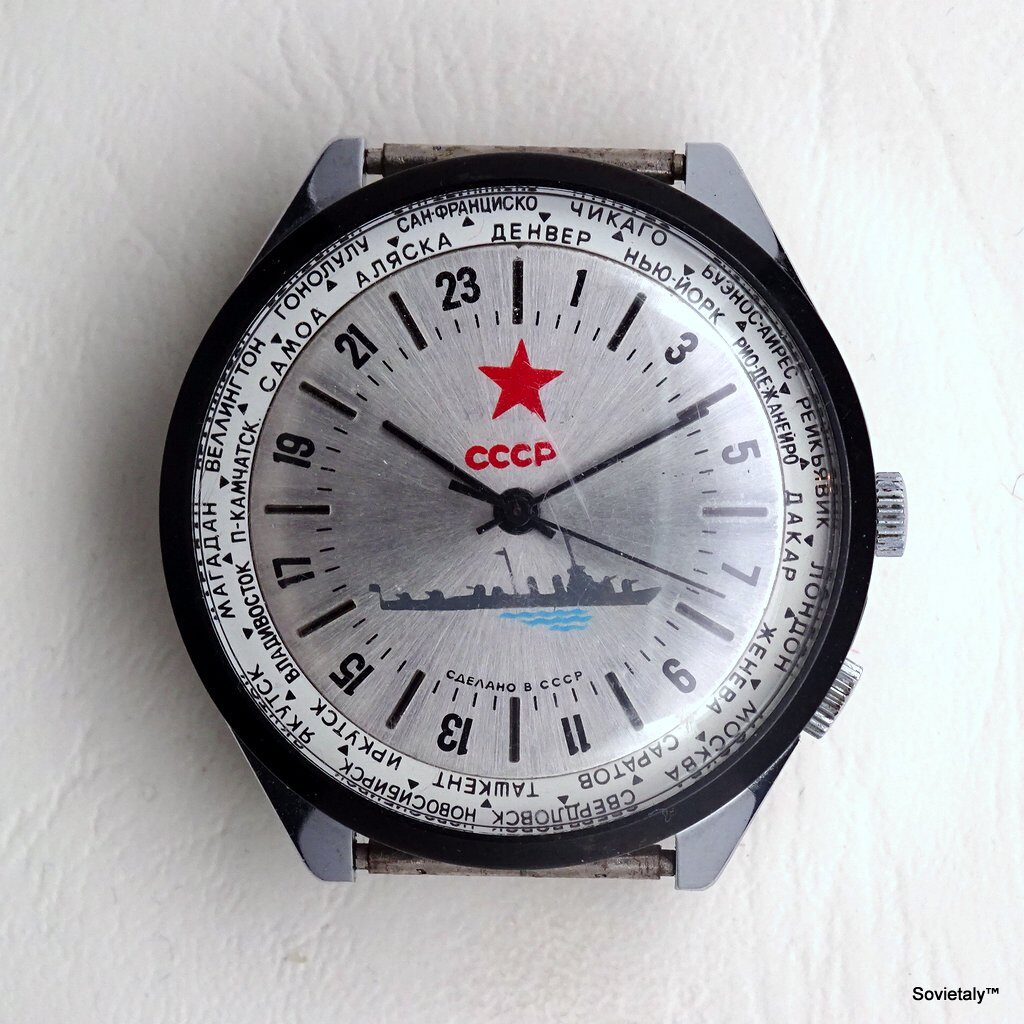
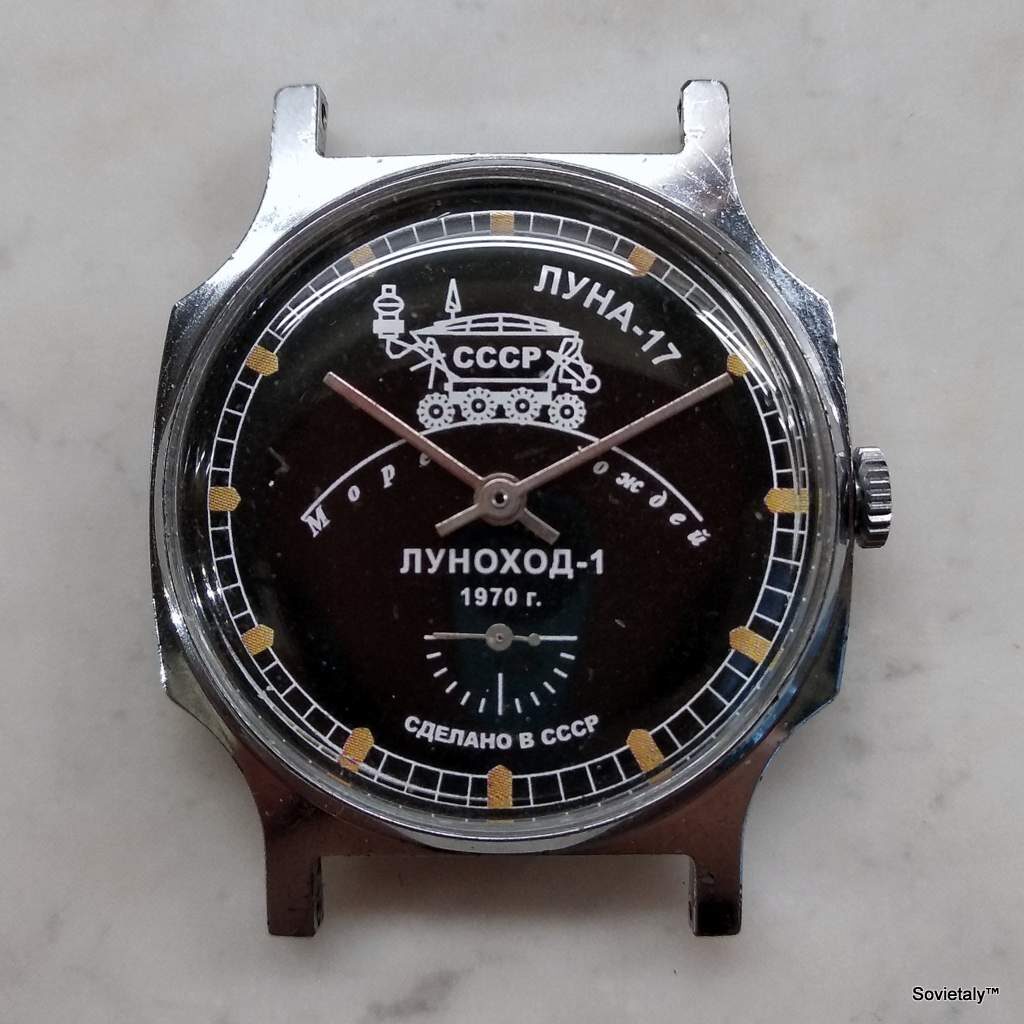
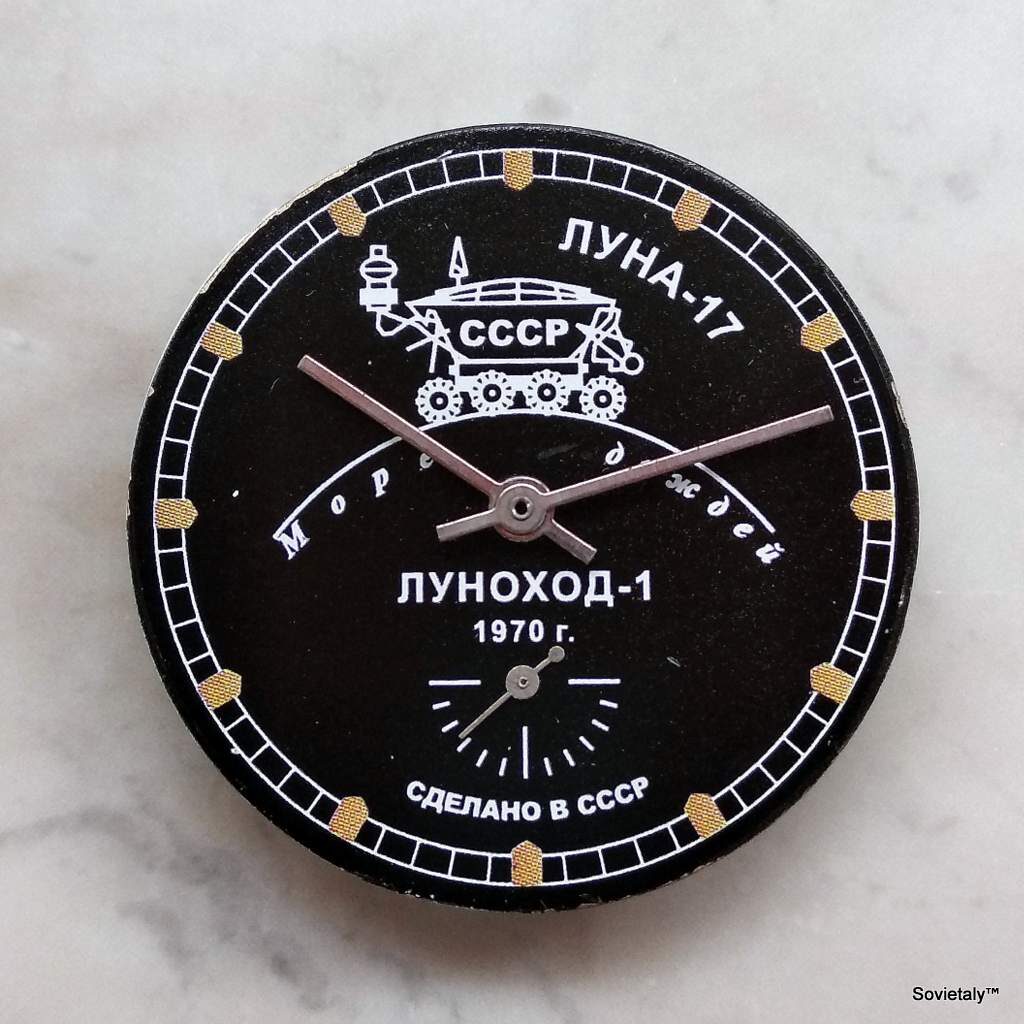
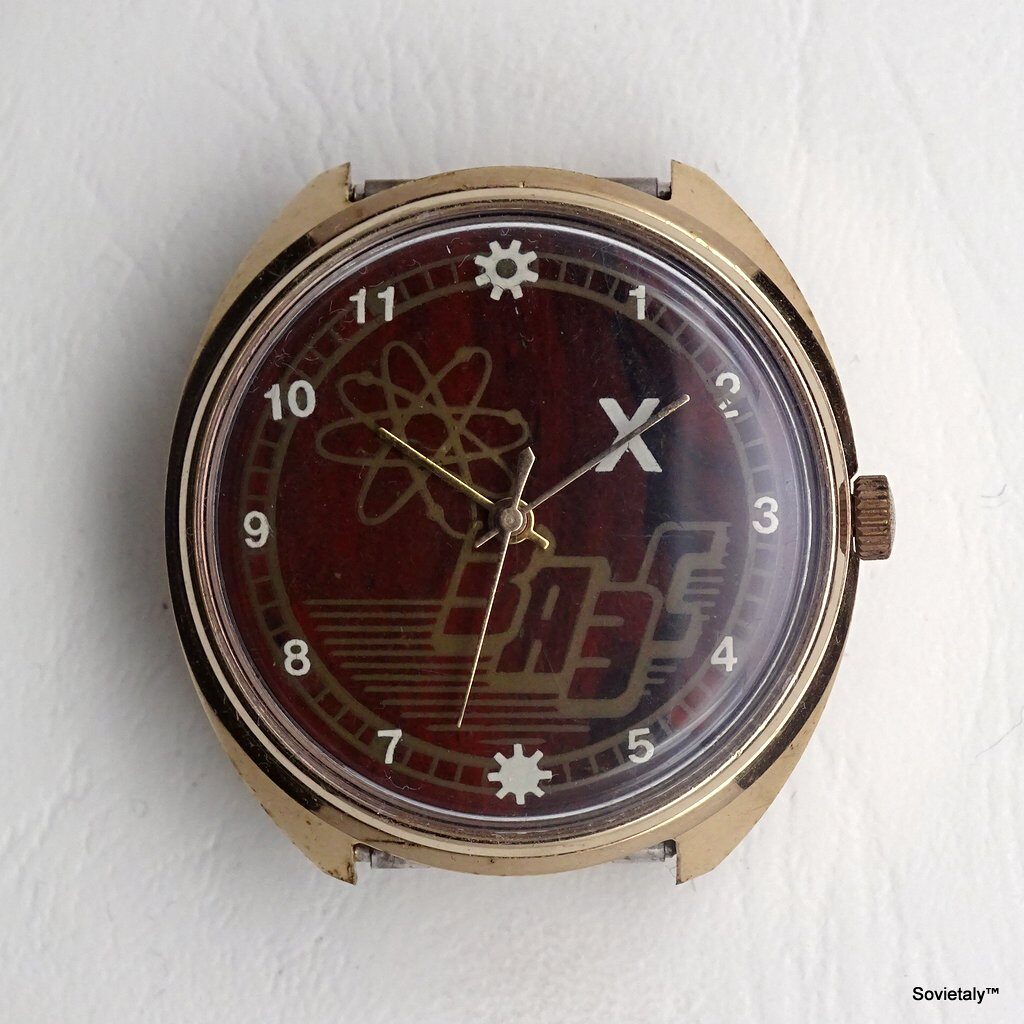
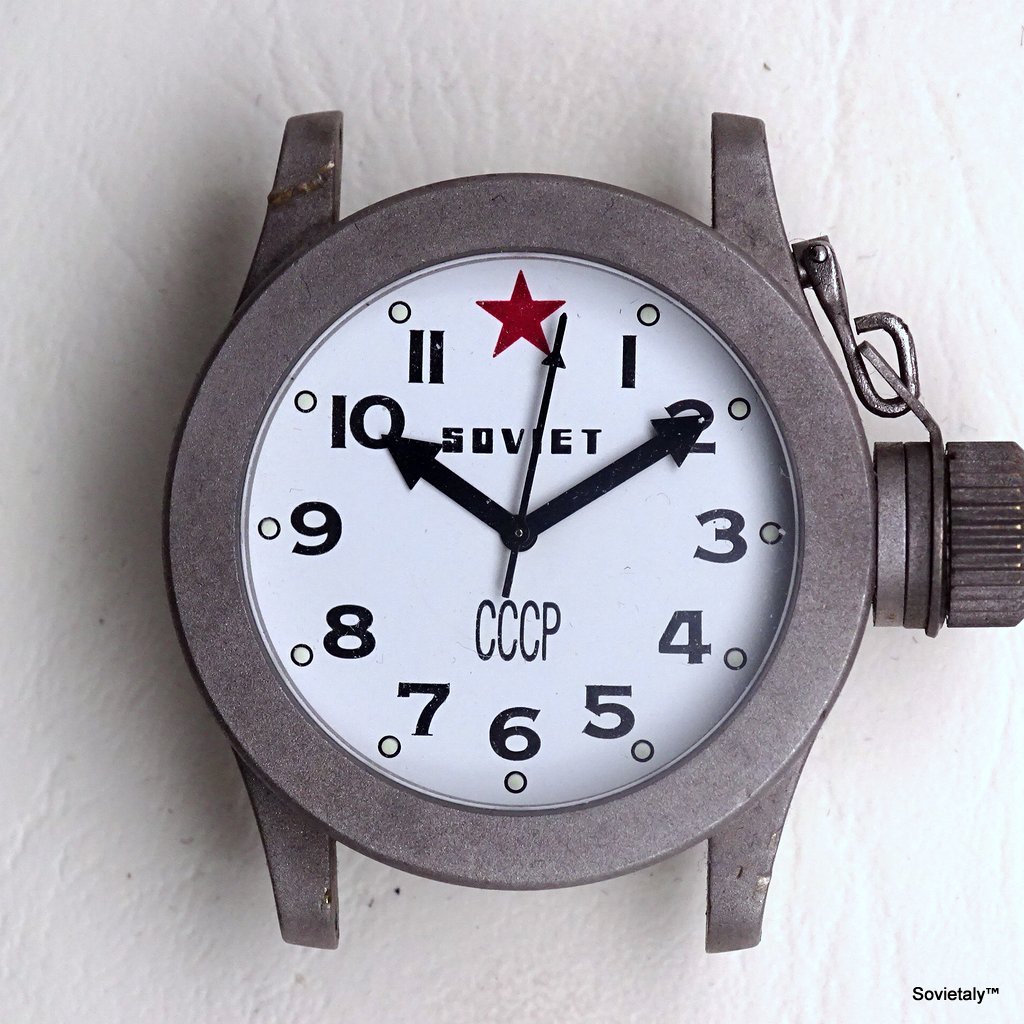
In the 1990s, the Soviet CCCP watch gained significant popularity, especially in Italy, due to its unique design and nostalgic connection to the Soviet era. These watches, although not directly produced in the USSR, utilised high-quality Russian movements and featured an aesthetic that strongly evoked the Soviet period.

Production and Movements of the Soviet CCCP Watch
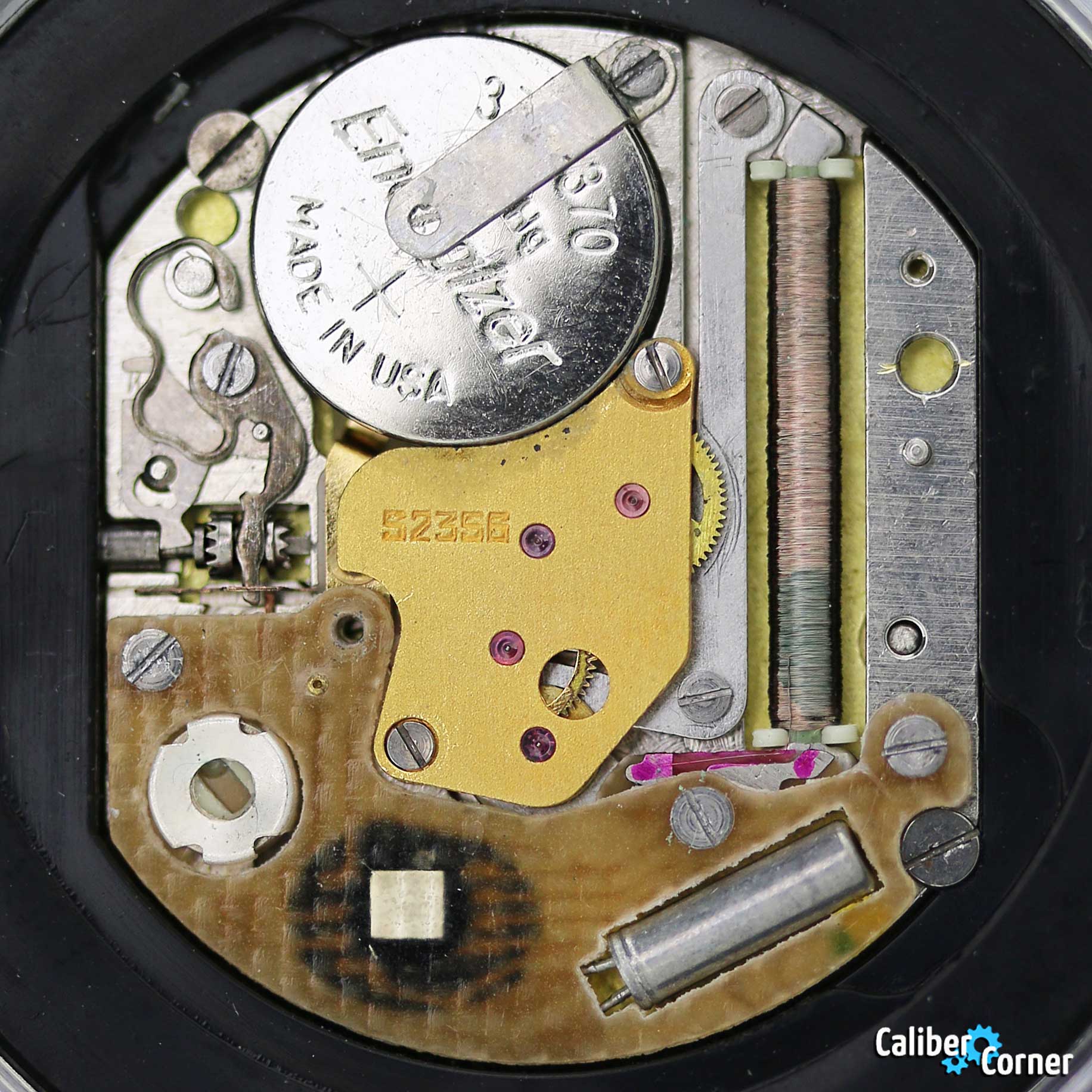
SOVIET watches were known for using a variety of mechanical and quartz movements produced by major Soviet factories. Among these, the Vostok 2414 and 2409 movements were particularly appreciated for their robustness and reliability. Additionally, Poljot calibres and Soviet quartz movements were also used. It is likely that the producers of the watch managed to purchase batches of movements from struggling ex-Soviet factories, ensuring high build quality
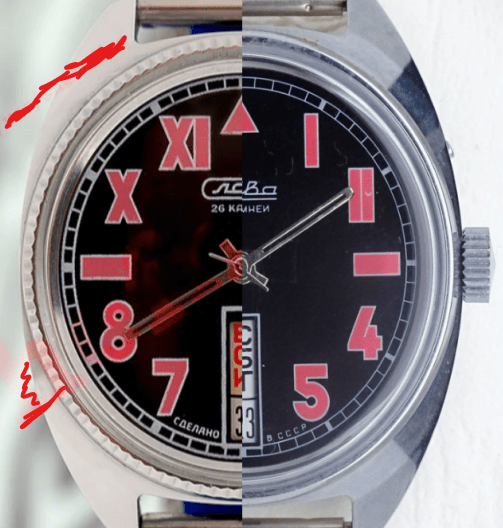
Some SOVIET watches also mimicked the crown closure design of Zlatoust watches, characterised by a screw-down cap that protected the actual crown. This design not only added a distinctive element but also increased crown protection, making the watch more resistant to external elements
Design and Features of the Soviet CCCP Watch
The design of the watch was heavily influenced by Soviet symbols and aesthetics. Many of these watches featured a red star on the dial, accompanied by the inscription “CCCP,” which stands for “Union of Soviet Socialist Republics” in Cyrillic. These design elements not only evoked the collective imagery of the era but also offered a sense of authenticity and nostalgia for the wearer. Each watch was a tribute to the glorious past of the Soviet Union
Distribution and Popularity of the Soviet CCCP Watch in Italy
During the 1990s, the watch was particularly popular in Italy. It was imported and distributed through specialised watch shops and vintage item retailers. Its popularity was due to the combination of a distinctive design and an affordable price, making it attractive to both collectors and vintage watch enthusiasts. Additionally, the allure of Soviet design, combined with the quality of the mechanical movements, made these watches particularly desirable
Production Hypotheses of the Soviet CCCP Watch
Despite the lack of detailed official documentation, there are several hypotheses about the production of the Soviet CCCP watch:
- External Assembly: It is possible that the Russian movements and components were assembled in facilities outside Russia, leveraging available resources and infrastructure in other countries to reduce costs and circumvent the economic difficulties of the post-Soviet period.
- Foreign Market: Another hypothesis is that the SOVIET brand was created specifically for foreign markets, such as Italy, exploiting the appeal of Soviet design to attract collectors and nostalgics without having to compete directly with established Russian watch brands
Conclusion on the Soviet CCCP Watch
The Soviet CCCP watch represents a fascinating chapter in the history of 1990s horology. With its Soviet-era inspired design and use of high-quality movements, this watch continues to be appreciated by collectors and enthusiasts worldwide. Although its production has ended, its charm persists, offering a piece of history and nostalgia to anyone who wears it.
For more information on the Soviet CCCP watch and other vintage Russian watches, we recommend exploring collector forums and historical archives online.
Sources:
- Raketa Big Zero: The Story Behind One of the Most Iconic Watches

- CCCP Sputnik 1 – A Watch That Celebrates the Space Age

- How to Remove Scratches from the Plexiglass of Your Watch: Complete Guide

- Complete Guide to Modern Russian Watchmaking

- Soviet CCCP Watch: The History of SOVIET Watches from the ’90s

- Russian Military Watches: A Comprehensive Guide