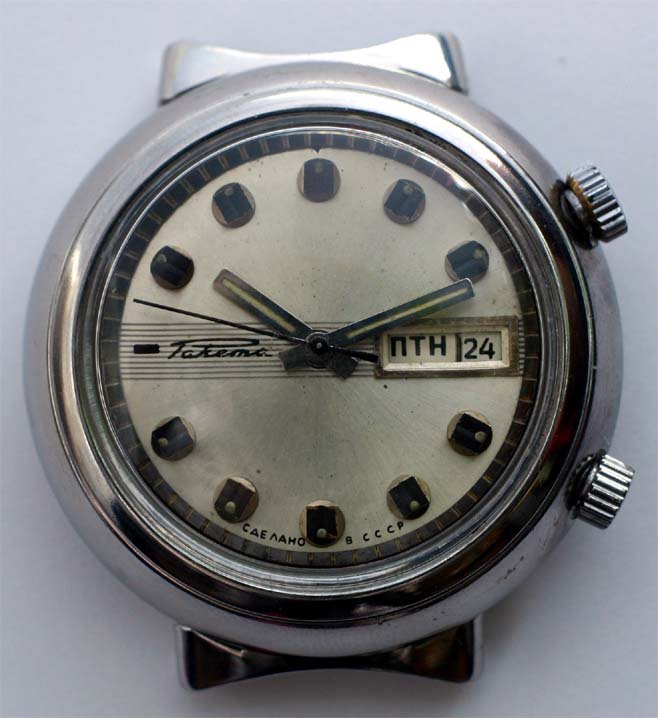
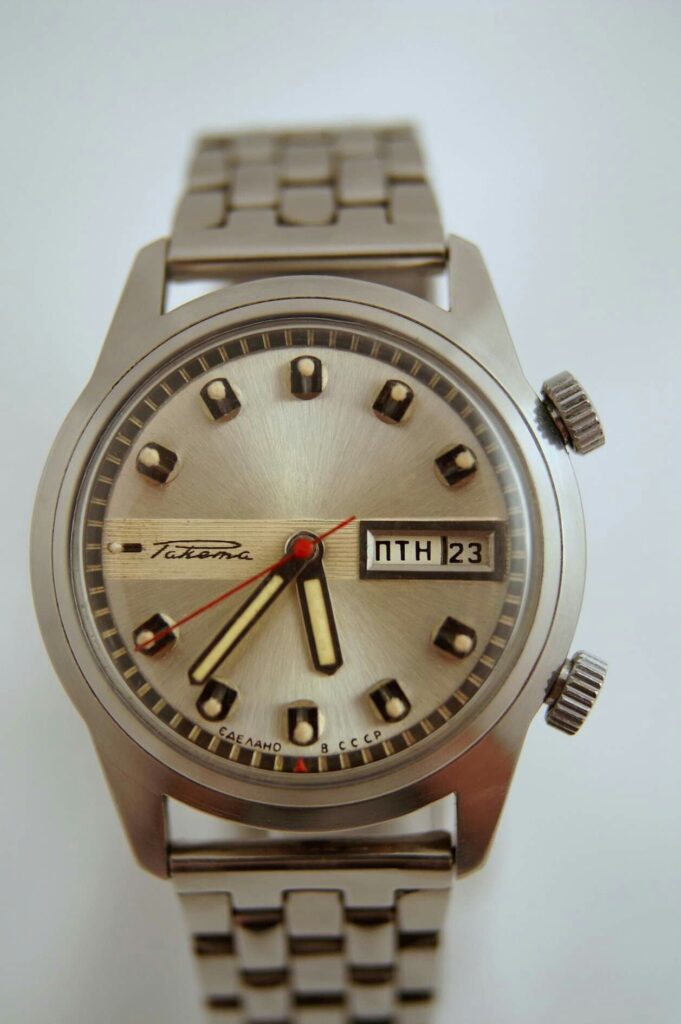
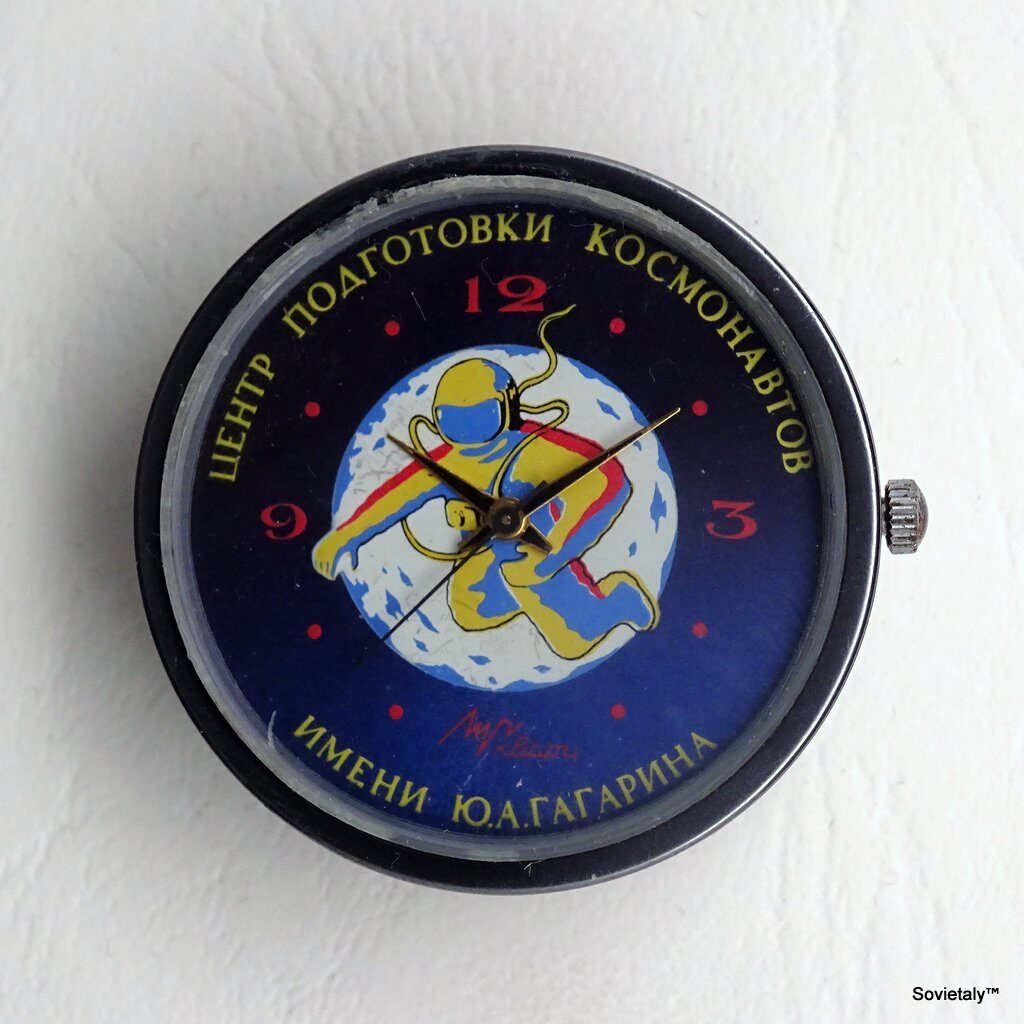
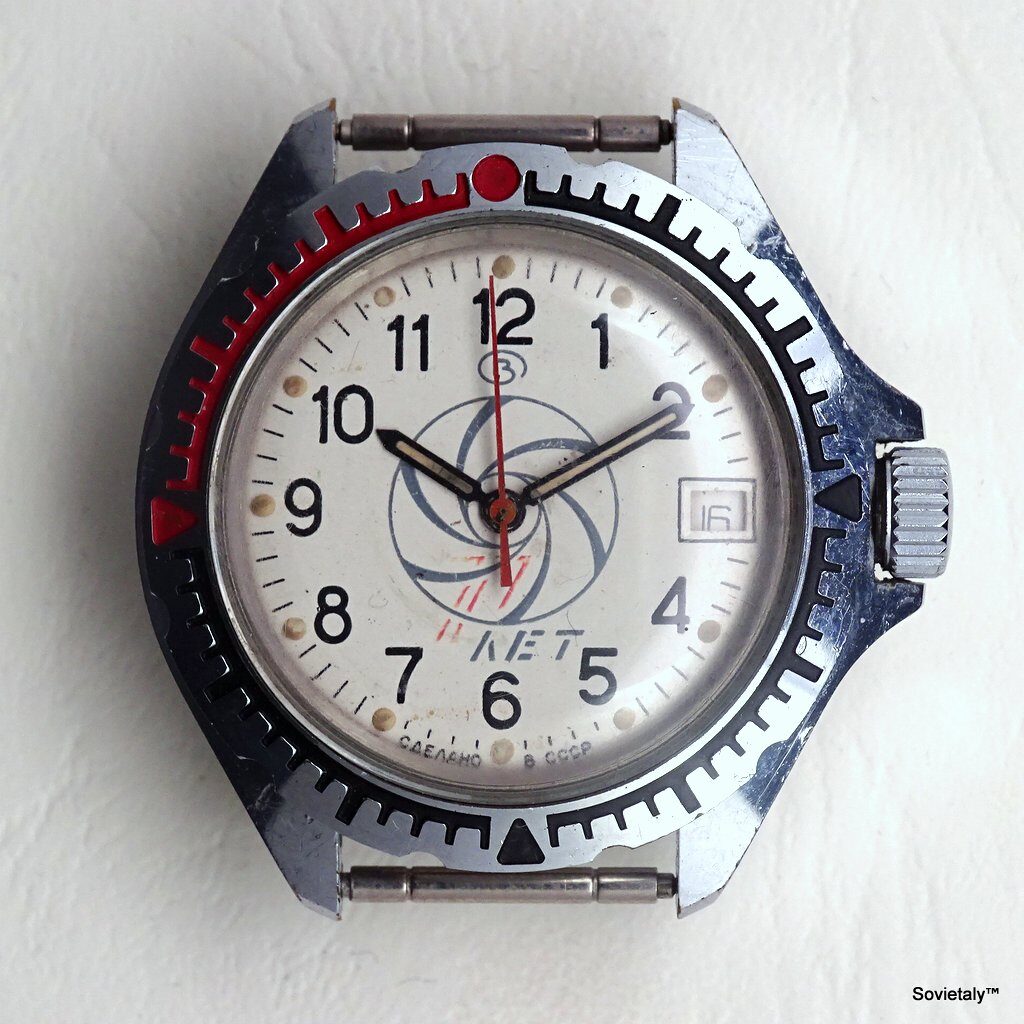
The Raketa Big Zero is an iconic watch produced by the Petrodvorets Watch Factory, Russia’s oldest watch manufacturer. Known for its unique and symbolic design, this model has sparked numerous speculations about its origin over the years. However, a Facebook post from July 20, 2021, by Александр Бродниковский, one of the most prominent Raketa watch collectors, finally sheds light on the true story behind its dial.

The Facebook Post
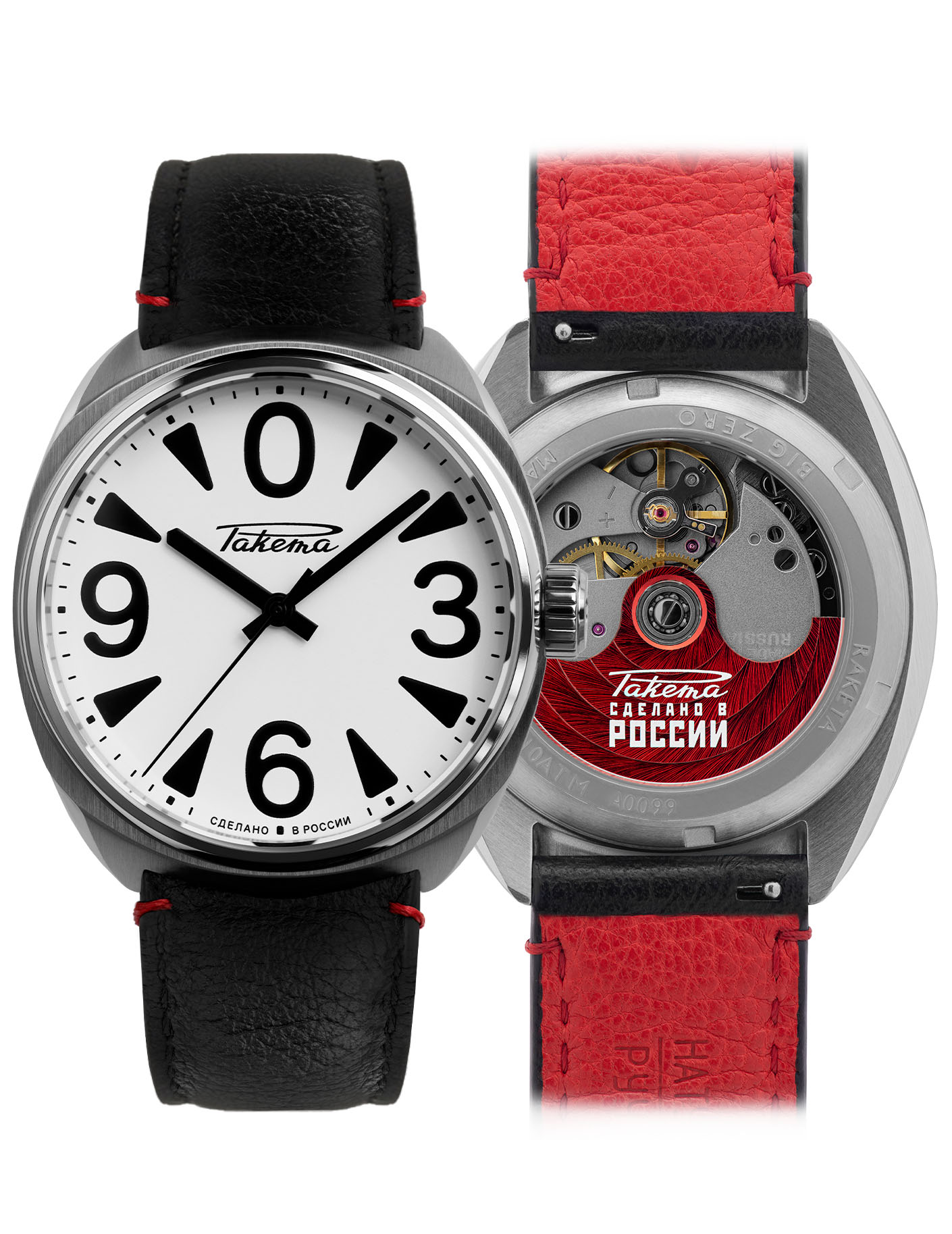
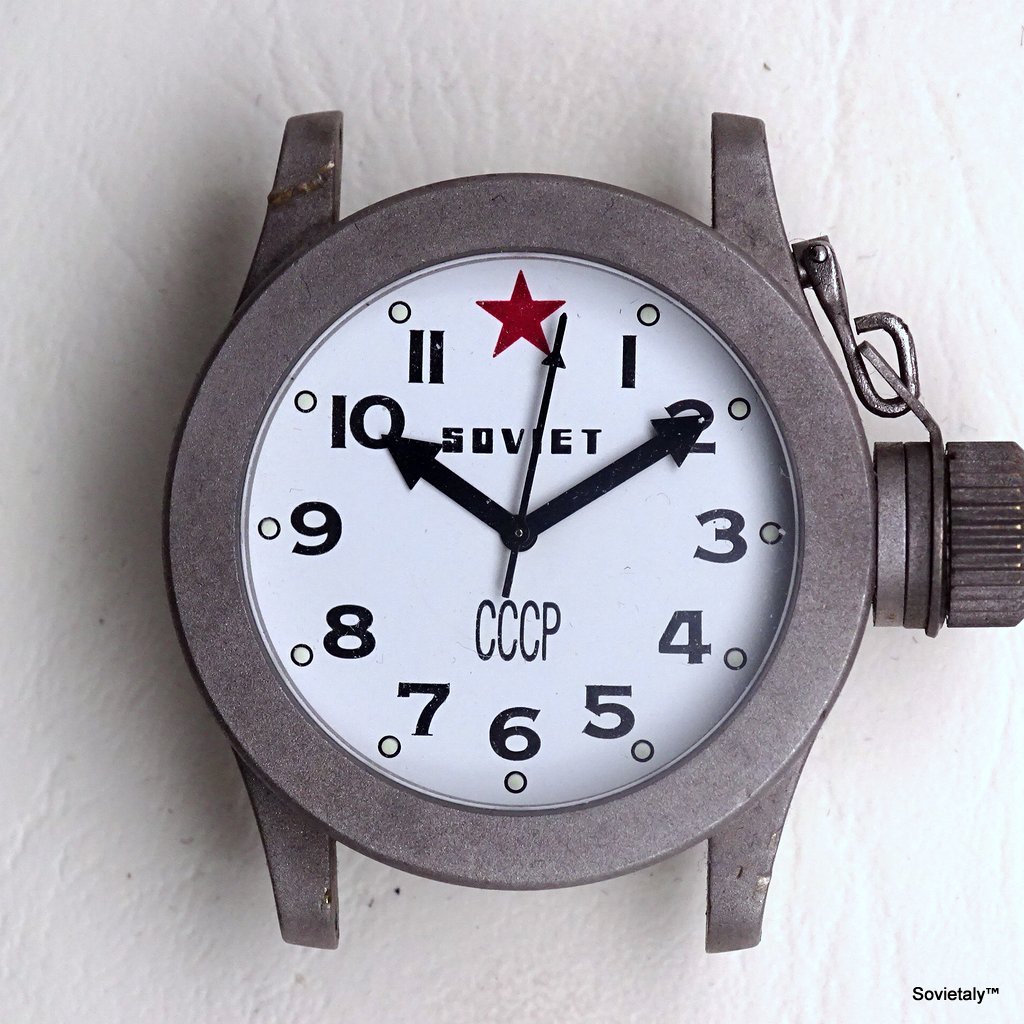
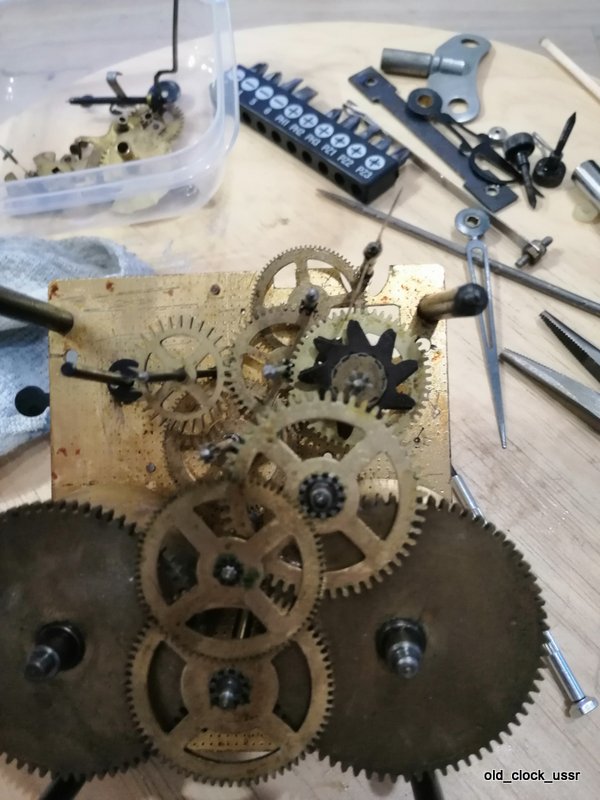
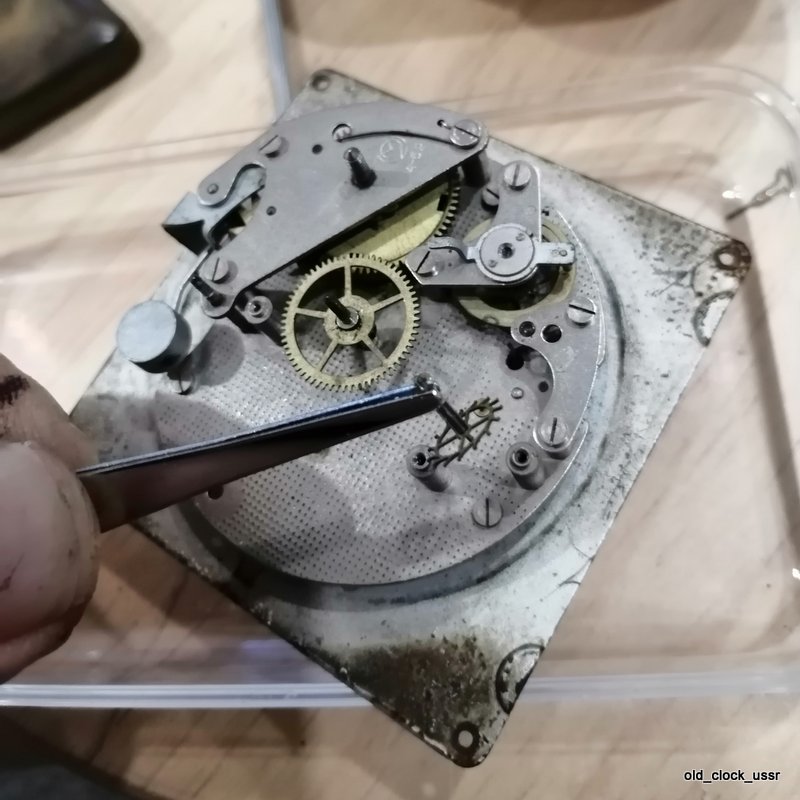
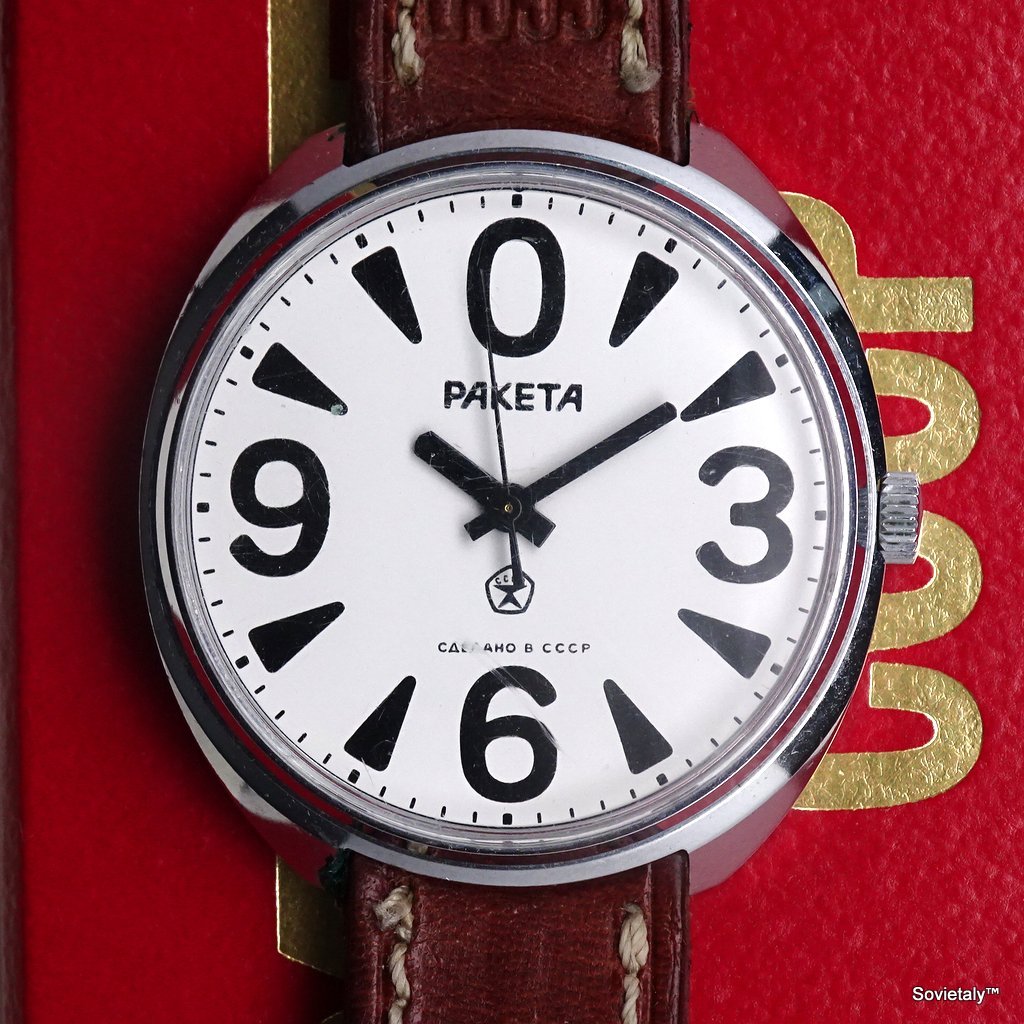
Часы «Ракета»-“нулевик” (“большой ноль”, “зеро”) Петродворцового Часового Завода на базовом калибре «Плоская Россия» 2609.НА в 51-м корпусе появились в 1984-1985 годах. По заказу Всесоюзного Общества Слепых (ВОС) для людей с ослабленным зрением был разработан дизайн часов с белым циферблатом, большими контрастными знаками и широкими стрелками.
К 1986-му году выпуск данной модели намечалось прекратить, поскольку для ВОС часов было выпущено достаточно, а обычным гражданам они были ни к чему. Началась перестройка. На Петродворцовый Часовой Завод приехали итальянские предприниматели. Часы с «обнулением» привели их в восторг. «Да ведь это же символ Перестройки! Горбачев начинает всё с нуля!», воскликнули итальянцы и сделали для себя огромный заказ, спрос на всё «перестроечное» на Западе тогда был весьма велик.
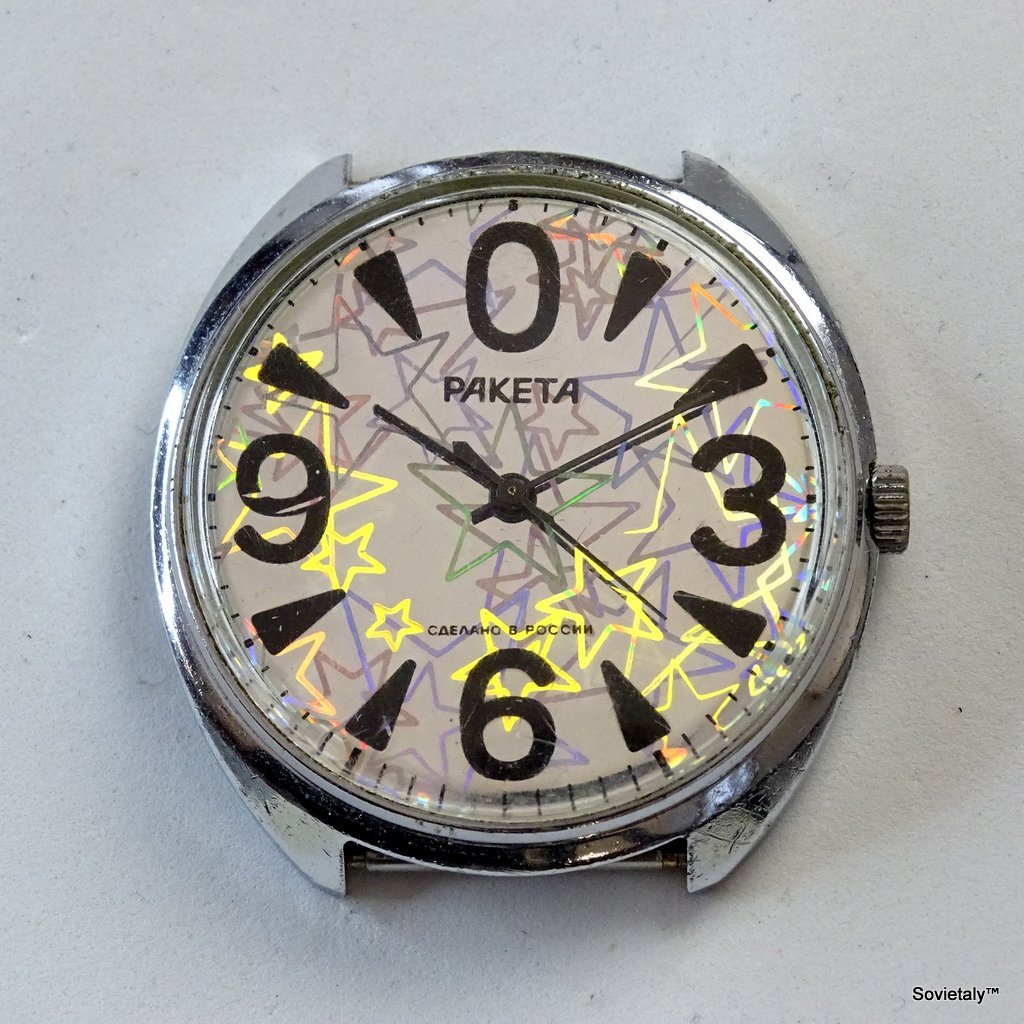
С этого момента на ПЧЗ начался выпуск всевозможных внешних оформлений «нулевика»: на тему перестройки (с изображениями советской символики), карманные, в классических корпусах, с чёрными циферблатами и даже с голографической пленкой на циферблате.
The Birth of the Raketa Big Zero
According to Александр Бродниковский (Alexander Brodnikovsky), the Raketa Big Zero, also known as “нулевик” or “большой ноль” in Russian, was introduced between 1984 and 1985. The model was developed upon request by the All-Soviet Society of the Blind (ВОС) to meet the needs of visually impaired individuals. As a result, the watch featured a white dial with large, high-contrast numbers and wide hands to enhance readability.
The Evolution of the Raketa Big Zero and its Encounter with the West
In 1986, after fulfilling the VOS’s requirements, the production of the Raketa Big Zero seemed destined to end. However, the arrival of several Italian entrepreneurs changed the course of history. They were captivated by the design of the watch, interpreting the large zero as a symbol of Perestroika, the reform period led by Gorbachev. Enthusiastically, they exclaimed, “This is the symbol of Perestroika! Gorbachev is starting everything from zero!” This interpretation led to a significant order, reigniting production.

This Western interest spurred the creation of new versions of the Raketa Big Zero, including various designs—some with Soviet symbols, pocket versions, black dials, and even holographic film-covered dials. The Raketa Big Zero became a symbol of transition, appreciated not only in its homeland but also abroad during one of the Soviet Union’s most turbulent periods.

The All-Soviet Society of the Blind (ВОС): A Social Pillar in the USSR
The Всесоюзное Общество Слепых (ВОС), known as the All-Soviet Society of the Blind, was founded in 1925 with the goal of improving the lives of blind individuals in the Soviet Union. This organization provided educational, employment, and social support, offering blind individuals tools and opportunities to integrate into the country’s economic and cultural life.
During the 1980s, VOS reached the peak of its influence, operating numerous factories where visually impaired individuals could work in protected environments. Products made under the VOS’s guidance included mechanical components, textiles, handicrafts, and even watches like the Raketa Big Zero, specifically designed for those with visual impairments. The watch, with its white dial, large, contrasting numbers, and wide hands, exemplified the VOS’s collaboration with Soviet industry to improve the quality of life for the visually impaired.
The VOS, during the Soviet period, was not only focused on providing jobs but also on supporting cultural and sporting initiatives. By the 1980s, the organization had over 150,000 members and managed schools, factories, and social centers for the blind, becoming a major pillar of Soviet welfare for the disabled.
This collaboration between the VOS and the Petrodvorets Watch Factory (ПЧЗ) led to the creation of a project initially intended to serve the visually impaired but which later gained broader significance during the Perestroika era.
Conclusion
Today, the Raketa Big Zero remains a beloved timepiece among collectors for its iconic design and unique history. Thanks to Александр Бродниковский (Alexander Brodnikovsky), we can now appreciate this watch not just as a mere timekeeper but as a symbol of an era of radical change.