How to Recognize Soviet and Russian Movements?
One of the key features of Soviet watches is that they contain only Soviet movements. These watches do not feature any external parts; all components were produced within the USSR. The quality of these movements varied depending on the factory, with some periods of excellence and others less so.
Here are some fundamental and curious pieces of information about these movements.
The Codes on Soviet Watch Passports
The codes used to identify Soviet movements were developed and standardized in the 1960s. These codes can be found on the passports that accompanied every watch produced during the Soviet era:
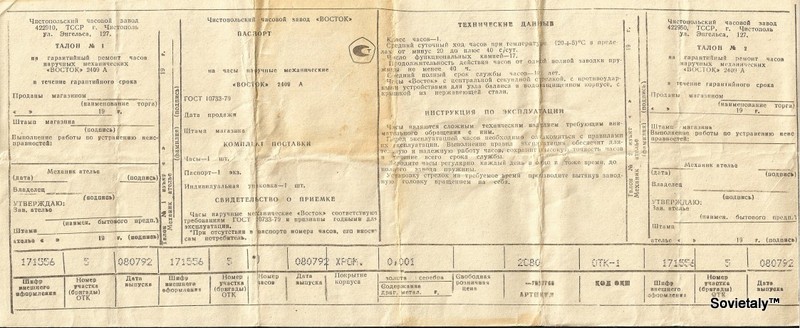

What Do the Codes Mean?
Deciphering the code is not particularly complicated. The movement code consists of 4 digits and one or two letters. After the fall of the Soviet Union, more codes were added, and the two digits often became three.
- The first two digits represent the movement’s diameter in millimeters.
- The next two/three digits represent the specific characteristics of the movement.
- The following letters represent the variations that occurred over time.
Movements with the same characteristics produced by different companies have the same code, but this does not mean they are identical. Usually, the movement is identified by the manufacturing company followed by the movement code.
A classic example found on many websites includes:
- Slava 2416
- Vostok 2416
- Poljot 2416
All three movements have a diameter of 24mm, and the 16 identifies them as:
- Automatic
- Central seconds
- Date
- Shockproof
For detailed characteristics of the movements, you can find an exhaustive list here.
Online Resources
There is another valuable online resource often used to identify movements and gain related information: Ranfft Watches.
Other useful resources include:
A good understanding of Russian/Soviet movements can often help quickly identify when a watch has been assembled or is not contemporaneous.
Examples of Movements
Some common Vostok movements include:
- Vostok 2409
- Vostok 2414A
- Vostok 2416b
For more detailed characteristics of these movements, you can refer to the Ranfft database.
Conclusion
The subject is vast and complex with many nuances. This guide aims to provide a brief introduction to help you start understanding the complexity of the Russian/Soviet watchmaking world.
All images of the movements can be found at: Ranfft Watches.





